Cello Sheet Music
 "Music expresses that which cannot be said and on which it is impossible to be silent. " Victor Hugo
"Music expresses that which cannot be said and on which it is impossible to be silent. " Victor Hugo
Ottorino Respighi

Ottorino Respighi (July 9, 1879, Bologna - April 18, 1936) was an Italian composer, musicologist and conductor. He is best known for his orchestral Roman trilogy: Fontane di Roma - "Fountains of Rome"; Pini di Roma - "Pines of Rome"; and Feste Romane - "Roman Festivals". His musicological interest in 16th-, 17th- and 18th-century music led him to also compose pieces based on the music of this period.
Born in Bologna, he studied composition with Giuseppe Martucci and Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov. Many sources indicate that he also studied briefly with Max Bruch, but in her biography of the composer, Respighi's wife asserts that this is not the case. Principally a violinist until 1908, he then turned primarily to composition. He lived in Rome from 1913.
Born in Bologna, he studied composition with Giuseppe Martucci and Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov. Many sources indicate that he also studied briefly with Max Bruch, but in her biography of the composer, Respighi's wife asserts that this is not the case. Principally a violinist until 1908, he then turned primarily to composition. He lived in Rome from 1913.
Mozart

Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, full name Johann Chrysostom Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 â 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical era. His over 600 compositions include works widely acknowledged as pinnacles of symphonic, concertante, chamber, piano, operatic, and choral music. Mozart is among the most enduringly popular of classical composers, and many of his works are part of the standard concert repertoire.
Mozart's music, like Haydn's, stands as an archetypal example of the Classical style. His works spanned the period during which that style transformed from one exemplified by the style galant to one that began to incorporate some of the contrapuntal complexities of the late Baroque, complexities against which the galant style had been a reaction. Mozart's own stylistic development closely paralleled the development of the classical style as a whole. In addition, he was a versatile composer and wrote in almost every major genre, including symphony, opera, the solo concerto, chamber music including string quartet and string quintet, and the piano sonata. While none of these genres were new, the piano concerto was almost single-handedly developed and popularized by Mozart. He also wrote a great deal of religious music, including masses; and he composed many dances, divertimenti, serenades, and other forms of light entertainment.
The central traits of the classical style can be identified in Mozart's music. Clarity, balance, and transparency are hallmarks of his work.
Mozart's music, like Haydn's, stands as an archetypal example of the Classical style. His works spanned the period during which that style transformed from one exemplified by the style galant to one that began to incorporate some of the contrapuntal complexities of the late Baroque, complexities against which the galant style had been a reaction. Mozart's own stylistic development closely paralleled the development of the classical style as a whole. In addition, he was a versatile composer and wrote in almost every major genre, including symphony, opera, the solo concerto, chamber music including string quartet and string quintet, and the piano sonata. While none of these genres were new, the piano concerto was almost single-handedly developed and popularized by Mozart. He also wrote a great deal of religious music, including masses; and he composed many dances, divertimenti, serenades, and other forms of light entertainment.
The central traits of the classical style can be identified in Mozart's music. Clarity, balance, and transparency are hallmarks of his work.
Jean-Baptiste Lully
Jean-Baptiste Lully (UK: /ˈlʊli/, US: /luːˈliː/; French: ; born Giovanni Battista Lulli, Italian: ; 28 November 1632 – 22 March 1687) was an Italian-born French composer, instrumentalist, and dancer who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he spent most of his life working in the court of Louis XIV of France and became a French subject in 1661.
Bernhard Cossmann

Bernhard Cossmann (17 May 1822 – 7 May 1910) was a German cellist. Born in Dessau, he first studied under Theodore Muller. During his life, he worked for the Grand Opera in Paris and became acquainted with Franz Liszt, with whom he went to Weimar. In 1866, Cossmann was appointed professor of cello studies at the Moscow Conservatory. However, in 1878, Cossmann helped found the Hoch Conservatory in Frankfurt, where he occupied the post of teacher of cello.Cossmann was not only a frequent soloist and quartet member, but was also a composer. His works include three fantasias, Tell, Euryanthe, and multiple solo works for various instruments. In addition, he composed many etudes and studies for the cello, many of which are still used today.
Max Richter

Max Richter (/ˈrɪktər/, /ˈrɪxtər/; German: ; born 22 March 1966) is a German-born British composer and pianist. He works within postminimalism and in the meeting of contemporary classical and alternative popular musical styles. Richter is classically trained, having graduated in composition from the Royal Academy of Music in London, and studied with Luciano Berio in Italy.
Ilio Volante

Was born in Italy in 1964, he was still a teen ager when he started his music studies (saxophone) showing from the very beginning a particular predisposition towards the music composition and Jazz music. At the age of 19 he won the audition for the Italian National Army Band stationed in Rome. He served it for 10 years under the direction of Col. Marino BARTOLONI. After this, he played in the Grenadiers of Sardinia’s Band (Rome) and the Shape International Band (the official Nato Band) stationed in Mons (BELGIUM). In this last post, he covered for three years the 1st Tenor Saxophone slot helping the Director, MSg Allen WITTIG, in doing the original arrangements for the Big Band. http://www.iliovolante.com http://www.musicaperbanda.com
Acoutic Cafe

Acoustic Café is an independent, syndicated radio program, produced in Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States. (Not to be confused with the Japanese instrumental group of the same name founded by Norihiro Tsuru.) Started in 1995, Acoustic Café presents singer-songwriters in various genres, playing songs in the Acoustic Café studio and chatting with host Rob Reinhart. A selection of current and past recorded material (on CDs) is also a part of each weekly program.
Bach

Johann Sebastian Bach (31 March 1685 – 28 July 1750) was a German composer and organist whose sacred and secular works for choir, orchestra, and solo instruments drew together the strands of the Baroque period and brought it to its ultimate maturity. Although he introduced no new forms, he enriched the prevailing German style with a robust contrapuntal technique, an unrivalled control of harmonic and motivic organisation in composition for diverse musical forces, and the adaptation of rhythms and textures from abroad, particularly Italy and France.
Revered for their intellectual depth and technical and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg concertos; the Goldberg Variations; the English Suites, French Suites, Partitas, and Well-Tempered Clavier; the Mass in B Minor; the St. Matthew Passion; the St. John Passion; The Musical Offering; The Art of Fugue; the Sonatas and Partitas for violin solo; the Cello Suites; more than 200 surviving cantatas; and a similar number of organ works, including the celebrated Toccata and Fugue in D Minor.
While Bach's fame as an organist was great during his lifetime, he was not particularly well-known as a composer. His adherence to Baroque forms and contrapuntal style was considered "old-fashioned" by his contemporaries, especially late in his career when the musical fashion tended towards Rococo and later Classical styles. A revival of interest and performances of his music began early in the 19th century, and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Revered for their intellectual depth and technical and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg concertos; the Goldberg Variations; the English Suites, French Suites, Partitas, and Well-Tempered Clavier; the Mass in B Minor; the St. Matthew Passion; the St. John Passion; The Musical Offering; The Art of Fugue; the Sonatas and Partitas for violin solo; the Cello Suites; more than 200 surviving cantatas; and a similar number of organ works, including the celebrated Toccata and Fugue in D Minor.
While Bach's fame as an organist was great during his lifetime, he was not particularly well-known as a composer. His adherence to Baroque forms and contrapuntal style was considered "old-fashioned" by his contemporaries, especially late in his career when the musical fashion tended towards Rococo and later Classical styles. A revival of interest and performances of his music began early in the 19th century, and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Ludwig van Beethoven

Ludwig van Beethoven (/ˈlʊdvɪɡ væn ˈbeɪt(h)oʊvən/ (About this soundlisten); German: (About this soundlisten); baptised 17 December 1770 – 26 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. A crucial figure in the transition between the classical and romantic eras in classical music, he remains one of the most recognized and influential musicians of this period, and is considered to be one of the greatest composers of all time.
Beethoven was born in Bonn, the capital of the Electorate of Cologne, and part of the Holy Roman Empire. He displayed his musical talents at an early age and was vigorously taught by his father Johann van Beethoven, and was later taught by composer and conductor Christian Gottlob Neefe. At age 21, he moved to Vienna and studied composition with Joseph Haydn. Beethoven then gained a reputation as a virtuoso pianist, and was soon courted by Prince Lichnowsky for compositions, which resulted in Opus 1 in 1795.
Beethoven was born in Bonn, the capital of the Electorate of Cologne, and part of the Holy Roman Empire. He displayed his musical talents at an early age and was vigorously taught by his father Johann van Beethoven, and was later taught by composer and conductor Christian Gottlob Neefe. At age 21, he moved to Vienna and studied composition with Joseph Haydn. Beethoven then gained a reputation as a virtuoso pianist, and was soon courted by Prince Lichnowsky for compositions, which resulted in Opus 1 in 1795.
Paul Stookey

Noel Paul Stookey (born December 30, 1937 in Baltimore, MD) is a singer-songwriter best known as Paul in the folk trio Peter, Paul and Mary. He took the stage name "Paul" as part of the trio Peter, Paul and Mary, but he has been known as Noel (his first name) otherwise, throughout his life. Since the death of Mary Travers, he has continued to work as a solo singer and activist.
Schubert

Franz Peter Schubert (January 31, 1797 – November 19, 1828) was an Austrian composer. He wrote some 600 lieder, nine symphonies (including the famous "Unfinished Symphony"), liturgical music, operas, and a large body of chamber and solo piano music. He is particularly noted for his original melodic and harmonic writing.
While Schubert had a close circle of friends and associates who admired his work (including his teacher Antonio Salieri, and the prominent singer Johann Michael Vogl), wider appreciation of his music during his lifetime was limited at best. He was never able to secure adequate permanent employment, and for most of his career he relied on the support of friends and family. Interest in Schubert's work increased dramatically in the decades following his death and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
While he was clearly influenced by the Classical sonata forms of Beethoven and Mozart (his early works, among them notably the 5th Symphony, are particularly Mozartean), his formal structures and his developments tend to give the impression more of melodic development than of harmonic drama. This combination of Classical form and long-breathed Romantic melody sometimes lends them a discursive style: his 9th Symphony was described by Robert Schumann as running to "heavenly lengths". His harmonic innovations include movements in which the first section ends in the key of the subdominant rather than the dominant (as in the last movement of the Trout Quintet). Schubert's practice here was a forerunner of the common Romantic technique of relaxing, rather than raising, tension in the middle of a movement, with final resolution postponed to the very end.
While Schubert had a close circle of friends and associates who admired his work (including his teacher Antonio Salieri, and the prominent singer Johann Michael Vogl), wider appreciation of his music during his lifetime was limited at best. He was never able to secure adequate permanent employment, and for most of his career he relied on the support of friends and family. Interest in Schubert's work increased dramatically in the decades following his death and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
While he was clearly influenced by the Classical sonata forms of Beethoven and Mozart (his early works, among them notably the 5th Symphony, are particularly Mozartean), his formal structures and his developments tend to give the impression more of melodic development than of harmonic drama. This combination of Classical form and long-breathed Romantic melody sometimes lends them a discursive style: his 9th Symphony was described by Robert Schumann as running to "heavenly lengths". His harmonic innovations include movements in which the first section ends in the key of the subdominant rather than the dominant (as in the last movement of the Trout Quintet). Schubert's practice here was a forerunner of the common Romantic technique of relaxing, rather than raising, tension in the middle of a movement, with final resolution postponed to the very end.
Music theory

Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. The Oxford Companion to Music describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory"
Saint Saens
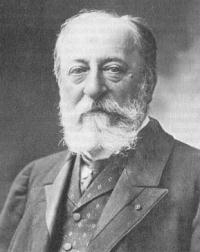
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (9 October 1835 – 16 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor, and pianist, known especially for The Carnival of the Animals, Danse Macabre, Samson and Delilah, Havanaise, Introduction and Rondo capriccioso, and his Symphony No. 3 (Organ Symphony).
Yves Montand

Ivo Livi (Italian pronunciation: ), better known as Yves Montand (French: ; 13 October 1921 – 9 November 1991), was an Italian-French actor and singer.Montand was born Ivo Livi in Monsummano Terme, Italy, to Giovanni Livi, a broom manufacturer, and Giuseppina Simoni, a devout Catholic, while her husband held strong Communist beliefs. Montand's family left for France in 1923 because of Italy's Fascist regime. He grew up in Marseille, where, as a young man, he worked in his sister's beauty salon (Salon de Coiffure), and later on the docks. He began a career in show business as a music-hall singer. In 1944, he was discovered by Édith Piaf in Paris and she made him part of her act.
Robert Hu

Robert Hu Musical artist Genre: Pop Songs Apricity Apricity · 2021 What about me? What about me? · 2021 Honey Latte
Honey Latte · 2021
Honey Latte · 2021
Igor Stravinsky

Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky (17 June 1882 – 6 April 1971) was a Russian-born, naturalised French, later naturalised American composer, pianist, and conductor.
He is widely acknowledged as one of the most important and influential composers of 20th century music. He was a quintessentially cosmopolitan Russian who was named by Time magazine as one of the 100 most influential people of the century. He became a naturalised French citizen in 1934 and a naturalized US citizen in 1945. In addition to the recognition he received for his compositions, he also achieved fame as a pianist and a conductor, often at the premieres of his works.
Stravinsky's compositional career was notable for its stylistic diversity. He first achieved international fame with three ballets commissioned by the impresario Sergei Diaghilev and performed by Diaghilev's Ballets Russes (Russian Ballets): The Firebird (1910), Petrushka (1911/1947), and The Rite of Spring (1913). The Rite, whose premiere provoked a riot, transformed the way in which subsequent composers thought about rhythmic structure, and was largely responsible for Stravinsky's enduring reputation as a musical revolutionary, pushing the boundaries of musical design.
After this first Russian phase Stravinsky turned to neoclassicism in the 1920s. The works from this period tended to make use of traditional musical forms (concerto grosso, fugue, symphony), frequently concealed a vein of intense emotion beneath a surface appearance of detachment or austerity, and often paid tribute to the music of earlier masters, for example J.S. Bach and Tchaikovsky.
In the 1950s he adopted serial procedures, using the new techniques over his last twenty years. Stravinsky's compositions of this period share traits with examples of his earlier output: rhythmic energy, the construction of extended melodic ideas out of a few two- or three-note cells, and clarity of form, of instrumentation, and of utterance.
He also published a number of books throughout his career, almost always with the aid of a collaborator, sometimes uncredited. In his 1936 autobiography, Chronicles of My Life, written with the help of Walter Nouvel, Stravinsky included his well-known statement that "music is, by its very nature, essentially powerless to express anything at all." With Alexis Roland-Manuel and Pierre Souvtchinsky he wrote his 1939–40 Harvard University Charles Eliot Norton Lectures, which were delivered in French and later collected under the title Poétique musicale in 1942 (translated in 1947 as Poetics of Music). Several interviews in which the composer spoke to Robert Craft were published as Conversations with Igor Stravinsky. They collaborated on five further volumes over the following decade.
He is widely acknowledged as one of the most important and influential composers of 20th century music. He was a quintessentially cosmopolitan Russian who was named by Time magazine as one of the 100 most influential people of the century. He became a naturalised French citizen in 1934 and a naturalized US citizen in 1945. In addition to the recognition he received for his compositions, he also achieved fame as a pianist and a conductor, often at the premieres of his works.
Stravinsky's compositional career was notable for its stylistic diversity. He first achieved international fame with three ballets commissioned by the impresario Sergei Diaghilev and performed by Diaghilev's Ballets Russes (Russian Ballets): The Firebird (1910), Petrushka (1911/1947), and The Rite of Spring (1913). The Rite, whose premiere provoked a riot, transformed the way in which subsequent composers thought about rhythmic structure, and was largely responsible for Stravinsky's enduring reputation as a musical revolutionary, pushing the boundaries of musical design.
After this first Russian phase Stravinsky turned to neoclassicism in the 1920s. The works from this period tended to make use of traditional musical forms (concerto grosso, fugue, symphony), frequently concealed a vein of intense emotion beneath a surface appearance of detachment or austerity, and often paid tribute to the music of earlier masters, for example J.S. Bach and Tchaikovsky.
In the 1950s he adopted serial procedures, using the new techniques over his last twenty years. Stravinsky's compositions of this period share traits with examples of his earlier output: rhythmic energy, the construction of extended melodic ideas out of a few two- or three-note cells, and clarity of form, of instrumentation, and of utterance.
He also published a number of books throughout his career, almost always with the aid of a collaborator, sometimes uncredited. In his 1936 autobiography, Chronicles of My Life, written with the help of Walter Nouvel, Stravinsky included his well-known statement that "music is, by its very nature, essentially powerless to express anything at all." With Alexis Roland-Manuel and Pierre Souvtchinsky he wrote his 1939–40 Harvard University Charles Eliot Norton Lectures, which were delivered in French and later collected under the title Poétique musicale in 1942 (translated in 1947 as Poetics of Music). Several interviews in which the composer spoke to Robert Craft were published as Conversations with Igor Stravinsky. They collaborated on five further volumes over the following decade.
Yuriy Leonovich

Born in Kyiv, Ukraine, cellist Yuriy Leonovich immigrated to the United States with his family. His teachers include cellists Stephen Geber and Robert DeMaine, and composer James Hartway. Leonovich earned his Doctor of Musical Arts degree from the Cleveland Institute of Music. He is a recipient of the Hope and Stanley Adelstein Prize for Excellence in Composition and Performance. Following his vision to expand the standard cello repertoire, Leonovich wrote his DMA research document on Gaspar Cassadó's cello concertos.
Keigo Hoashi

Keigo Hoashi is a composer, arranger and keyboardist. He was born in Meguro, Tokyo, Japan but moved to America after finishing high school. He graduated from the film music department at Berklee College of Music in Boston. He has been a member of the music production group MONACA since 2009.
Arcangelo Corelli

Arcangelo Corelli (17 February 1653 – 8 January 1713) was an Italian violinist and composer of Baroque music.
Corelli was born at Fusignano, in the current-day province of Ravenna, although at the time it was in the province of Ferrara. Little is known about his early life. His master on the violin was Giovanni Battista Bassani. Matteo Simonelli, the well-known singer of the pope’s chapel, taught him composition.
He gained his first major success in Paris at the age of nineteen, and to this he owed his European reputation. From Paris, Corelli went to Germany. In 1681 he was in the service of the electoral prince of Bavaria; between 1680 and 1685 he spent a considerable time in the house of his friend and fellow violinist-composer Cristiano Farinelli (believed to be the uncle of the celebrated castrato Farinelli).
In 1685 Corelli was in Rome, where he led the festival performances of music for Queen Christina of Sweden, and he was also a favorite of Cardinal Pietro Ottoboni, grandnephew of another Cardinal Pietro Ottoboni, who in 1689 became Pope Alexander VIII. From 1689 to 1690 he was in Modena; the Duke of Modena was generous to him. In 1708 he returned to Rome, living in the palace of Cardinal Ottoboni. His visit to Naples, at the invitation of the king, took place in the same year.
The style of execution introduced by Corelli and preserved by his pupils, such as Francesco Geminiani, Pietro Locatelli, and many others, was of vital importance for the development of violin playing. It has been said that the paths of all of the famous violinist-composers of 18th-century Italy led to Arcangelo Corelli who was their "iconic point of reference." (Toussaint Loviko, in the program notes to Italian Violin Concertos, Veritas, 2003)
Corelli was born at Fusignano, in the current-day province of Ravenna, although at the time it was in the province of Ferrara. Little is known about his early life. His master on the violin was Giovanni Battista Bassani. Matteo Simonelli, the well-known singer of the pope’s chapel, taught him composition.
He gained his first major success in Paris at the age of nineteen, and to this he owed his European reputation. From Paris, Corelli went to Germany. In 1681 he was in the service of the electoral prince of Bavaria; between 1680 and 1685 he spent a considerable time in the house of his friend and fellow violinist-composer Cristiano Farinelli (believed to be the uncle of the celebrated castrato Farinelli).
In 1685 Corelli was in Rome, where he led the festival performances of music for Queen Christina of Sweden, and he was also a favorite of Cardinal Pietro Ottoboni, grandnephew of another Cardinal Pietro Ottoboni, who in 1689 became Pope Alexander VIII. From 1689 to 1690 he was in Modena; the Duke of Modena was generous to him. In 1708 he returned to Rome, living in the palace of Cardinal Ottoboni. His visit to Naples, at the invitation of the king, took place in the same year.
The style of execution introduced by Corelli and preserved by his pupils, such as Francesco Geminiani, Pietro Locatelli, and many others, was of vital importance for the development of violin playing. It has been said that the paths of all of the famous violinist-composers of 18th-century Italy led to Arcangelo Corelli who was their "iconic point of reference." (Toussaint Loviko, in the program notes to Italian Violin Concertos, Veritas, 2003)
Vladimir Zubitsky

Vladimir Zubitsky is a well known composer of original accordion music. His more famous compositions include Children Suite No. 1, Karpatskaya Suite, Partite Concertata in Mode Jazz-Improvisazione, which are perform
Jean Sibelius

Jean Sibelius ( pronunciation (help·info)) (8 December 1865 – 20 September 1957) was a Finnish composer of the later Romantic period whose music played an important role in the formation of the Finnish national identity. His mastery of the orchestra has been described as "prodigious."
The core of Sibelius's oeuvre is his set of seven symphonies. Like Beethoven, Sibelius used each successive work to further develop his own personal compositional style. His works continue to be performed frequently in the concert hall and are often recorded.
In addition to the symphonies, Sibelius's best-known compositions include Finlandia, the Karelia Suite, Valse triste, the Violin Concerto in D minor and The Swan of Tuonela (one of the four movements of the Lemminkäinen Suite). Other works include pieces inspired by the Finnish national epic, the Kalevala; over 100 songs for voice and piano; incidental music for 13 plays; the opera Jungfrun i tornet (The Maiden in the Tower); chamber music; piano music; Masonic ritual music; and 21 separate publications of choral music.
The core of Sibelius's oeuvre is his set of seven symphonies. Like Beethoven, Sibelius used each successive work to further develop his own personal compositional style. His works continue to be performed frequently in the concert hall and are often recorded.
In addition to the symphonies, Sibelius's best-known compositions include Finlandia, the Karelia Suite, Valse triste, the Violin Concerto in D minor and The Swan of Tuonela (one of the four movements of the Lemminkäinen Suite). Other works include pieces inspired by the Finnish national epic, the Kalevala; over 100 songs for voice and piano; incidental music for 13 plays; the opera Jungfrun i tornet (The Maiden in the Tower); chamber music; piano music; Masonic ritual music; and 21 separate publications of choral music.
Jaroslav Jezek

Jaroslav Jezek (September 25, 1906 - January 1, 1942) was a Czech composer, pianist and conductor, author of jazz, classical, incidental and film music.Ježek was born in the Prague quarter of Žižkov to the family of a tailor. He was almost blind from a young age. He studied composition at the Prague Conservatory as a pupil of Karel Boleslav Jirák (1924–1927), at the master school of composition with Josef Suk (1927–1930)
Tchaikovsky

Pyotr Il'yich Tchaikovsky (May 7 1840 â November 6 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic era. While not part of the nationalistic music group known as "The Five", Tchaikovsky wrote music which, in the opinion of Harold Schonberg, was distinctly Russian: plangent, introspective, with modally-inflected melody and harmony.
Aesthetically, Tchaikovsky remained open to all aspects of Saint Petersburg musical life. He was impressed by Serov and Balakirev as well as the classical values upheld by the conservatory. Both the progressive and conservative camps in Russian music at the time attempted to win him over. Tchaikovsky charted his compositional course between these two factions, retaining his individuality as a composer as well as his Russian identity. In this he was influenced by the ideals of his teacher Nikolai Rubinstein and Nikolai's brother Anton.
Tchaikovsky's musical cosmopolitanism led him to be favored by many Russian music-lovers over the "Russian" harmonies and styles of Mussorgsky, Borodin and Rimsky-Korsakov.
Nonetheless he frequently adapted Russian traditional melodies and dance forms in his music, which enhanced his success in his home country. The success in St. Petersburg at the premiere of his Third Orchestral Suite may have been due in large part to his concluding the work with a polonaise. He also used a polonaise for the final movement of his Third Symphony.
Aesthetically, Tchaikovsky remained open to all aspects of Saint Petersburg musical life. He was impressed by Serov and Balakirev as well as the classical values upheld by the conservatory. Both the progressive and conservative camps in Russian music at the time attempted to win him over. Tchaikovsky charted his compositional course between these two factions, retaining his individuality as a composer as well as his Russian identity. In this he was influenced by the ideals of his teacher Nikolai Rubinstein and Nikolai's brother Anton.
Tchaikovsky's musical cosmopolitanism led him to be favored by many Russian music-lovers over the "Russian" harmonies and styles of Mussorgsky, Borodin and Rimsky-Korsakov.
Nonetheless he frequently adapted Russian traditional melodies and dance forms in his music, which enhanced his success in his home country. The success in St. Petersburg at the premiere of his Third Orchestral Suite may have been due in large part to his concluding the work with a polonaise. He also used a polonaise for the final movement of his Third Symphony.
George Handel
George Frideric Handel was a German, later British, Baroque composer who spent the bulk of his career in London, becoming well known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, and organ concertos
Hector Berlioz

Hector Berlioz (December 11, 1803 – March 8, 1869) was a French Romantic composer, best known for his compositions Symphonie fantastique and Grande messe des morts (Requiem). Berlioz made significant contributions to the modern orchestra with his Treatise on Instrumentation. He specified huge orchestral forces for some of his works; as a conductor, he performed several concerts with more than 1,000 musicians. He also composed around 50 songs. His influence was critical for the further development of Romanticism, especially in composers like Richard Wagner, Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov, Franz Liszt, Richard Strauss, Gustav Mahler and many others.
Placido Abela

Placido Abela Musical composer Born: 1814 Died: July 6, 1876, Abbey of Montecassino, Italy.
Felix Mendelssohn

Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy, born, and generally known in English-speaking countries, as Felix Mendelssohn (February 3, 1809 – November 4, 1847) was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic period.
The grandson of the philosopher Moses Mendelssohn, he was born into a notable Jewish family, although he himself was brought up initially without religion, and later as a Lutheran. He was recognized early as a musical prodigy, but his parents were cautious and did not seek to capitalise on his abilities. Indeed his father was disinclined to allow Felix to follow a musical career until it became clear that he intended to seriously dedicate himself to it.
Early success in Germany was followed by travel throughout Europe; Mendelssohn was particularly well received in England as a composer, conductor and soloist, and his ten visits there, during which many of his major works were premiered, form an important part of his adult career. His essentially conservative musical tastes however set him apart from many of his more adventurous musical contemporaries such as Liszt, Wagner and Berlioz. The Conservatory he founded at Leipzig became a bastion of this anti-radical outlook.
Mendelssohn's work includes symphonies, concerti, oratorios, piano and chamber music. He also had an important role in the revival of interest in the music of Johann Sebastian Bach. After a long period of relative denigration due to changing musical tastes and antisemitism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, his creative originality is now being recognized and re-evaluated. He is now among the most popular composers of the Romantic era.
The grandson of the philosopher Moses Mendelssohn, he was born into a notable Jewish family, although he himself was brought up initially without religion, and later as a Lutheran. He was recognized early as a musical prodigy, but his parents were cautious and did not seek to capitalise on his abilities. Indeed his father was disinclined to allow Felix to follow a musical career until it became clear that he intended to seriously dedicate himself to it.
Early success in Germany was followed by travel throughout Europe; Mendelssohn was particularly well received in England as a composer, conductor and soloist, and his ten visits there, during which many of his major works were premiered, form an important part of his adult career. His essentially conservative musical tastes however set him apart from many of his more adventurous musical contemporaries such as Liszt, Wagner and Berlioz. The Conservatory he founded at Leipzig became a bastion of this anti-radical outlook.
Mendelssohn's work includes symphonies, concerti, oratorios, piano and chamber music. He also had an important role in the revival of interest in the music of Johann Sebastian Bach. After a long period of relative denigration due to changing musical tastes and antisemitism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, his creative originality is now being recognized and re-evaluated. He is now among the most popular composers of the Romantic era.
Frederic Austin

Frederic William Austin (30 March 1872 – 10 April 1952) was an English baritone singer, a musical teacher and composer in the period 1905–30. He is best remembered for his restoration and production of The Beggar's Opera by John Gay and Johann Christoph Pepusch, and its sequel, Polly, in 1920–23. Austin was the older brother of the composer Ernest Austin (1874–1947).The standard melody for the carol "The Twelve Days of Christmas" was published by Austin in 1909. He arranged a traditional folk melody, adding a two-bar motif for "Five gold rings". He also altered the lyric, adding "on" at the beginning of each verse.
Friedrich Kuhlau

Friedrich Daniel Rudolf Kuhlau (German; Danish sometimes Frederick Kulav) (11 September 1786 – 12 March 1832) was a Danish pianist and composer during the late Classical and early Romantic periods. He was a central figure of the Danish Golden Age and is immortalized in Danish cultural history through his music for Elves' Hill, the first true work of Danish National Romanticism and a concealed tribute to the absolute monarchy. To this day it is his version of this melody which is the definitive arrangement.During his lifetime, Kuhlau was known primarily as a concert pianist and composer of Danish opera, but was responsible for introducing many of Beethoven's works, which he greatly admired, to Copenhagen audiences. Kuhlau was a prolific composer, as evidenced by the fact that although his house burned down, destroying all of his unpublished manuscripts, he still left a legacy of more than 200 published works in most genres.
Tom Kitt

Thomas Robert "Tom" Kitt (born 1974) is an American composer, conductor, orchestrator and musician. For his score for the musical Next to Normal, he shared the 2010 Pulitzer Prize for Drama with Brian Yorkey. He also won the Tony Award and 2008 Outer Critics Circle Award, and was nominated for a Drama Desk Award for American Idiot and Everyday Rapture.
Ernest Bloch

Ernest Bloch (July 24, 1880 – July 15, 1959) was a Swiss-born American composer. Bloch was a preeminent artist in his day, and left a lasting legacy. He is recognized as one of the greatest Swiss composers in history. As well as producing musical scores, Bloch had an academic career that culminated in his recognition as Professor Emeritus at the University of California, Berkeley in 1952.
Heitor Villa-Lobos

Heitor Villa-Lobos (March 5, 1887 – November 17, 1959) was a Brazilian composer, described as "the single most significant creative figure in 20th-century Brazilian art music". Villa-Lobos has become the best-known and most significant Latin American composer to date. He wrote numerous orchestral, chamber, instrumental and vocal works. His music was influenced by both Brazilian folk music and by stylistic elements from the European classical tradition, as exemplified by his Bachianas Brasileiras ("Brazilian Bachian-pieces").
His earliest pieces originated in guitar improvisations, for example Panqueca ("Pancake") of 1900. The concert series of 1915–21 included first performances of pieces demonstrating originality and virtuosic technique. Some of these pieces are early examples of elements of importance throughout his œuvre. His attachment to the Iberian Peninsula is demonstrated in Canção Ibéria of 1914 and in orchestral transcriptions of some of Enrique Granados' piano Goyescas (1918, now lost). Other themes that were to recur in his later work include the anguish and despair of the piece Desesperança— Sonata Phantastica e Capricciosa no. 1 (1915), a violin sonata including "histrionic and violently contrasting emotions", the birds of L'oiseau blessé d'une flèche (1913), the mother-child relationship (not usually a happy one in Villa-Lobos's music) in Les mères of 1914, and the flowers of Suíte floral for piano of 1916–18 which reappeared in Distribuição de flores for flute and guitar of 1937.
Reconciling European tradition and Brazilian influences was also an element that bore fruit more formally later. His earliest published work Pequena suíte for cello and piano of 1913 shows a love for the cello, but is not notably Brazilian, although it contains elements that were to resurface later. His three-movement String Quartet no. 1 (Suíte graciosa) of 1915 (expanded to six movements ca. 1947) is influenced by European opera, while Três danças características (africanas e indígenas) of 1914–16 for piano, later arranged for octet and subsequently orchestrated, is radically influenced by the tribal music of the Caripunas Indians of Mato Grosso.
With his tone poems Amazonas (1916, first performed in Paris in 1929) and Uirapurú (1916, first performed 1935) he created works dominated by indigenous Brazilian influences. The works use Brazilian folk tales and characters, imitations of the sounds of the jungle and its fauna, imitations of the sound of the nose-flute by the violinophone, and not least imitations of the uirapuru itself.
His earliest pieces originated in guitar improvisations, for example Panqueca ("Pancake") of 1900. The concert series of 1915–21 included first performances of pieces demonstrating originality and virtuosic technique. Some of these pieces are early examples of elements of importance throughout his œuvre. His attachment to the Iberian Peninsula is demonstrated in Canção Ibéria of 1914 and in orchestral transcriptions of some of Enrique Granados' piano Goyescas (1918, now lost). Other themes that were to recur in his later work include the anguish and despair of the piece Desesperança— Sonata Phantastica e Capricciosa no. 1 (1915), a violin sonata including "histrionic and violently contrasting emotions", the birds of L'oiseau blessé d'une flèche (1913), the mother-child relationship (not usually a happy one in Villa-Lobos's music) in Les mères of 1914, and the flowers of Suíte floral for piano of 1916–18 which reappeared in Distribuição de flores for flute and guitar of 1937.
Reconciling European tradition and Brazilian influences was also an element that bore fruit more formally later. His earliest published work Pequena suíte for cello and piano of 1913 shows a love for the cello, but is not notably Brazilian, although it contains elements that were to resurface later. His three-movement String Quartet no. 1 (Suíte graciosa) of 1915 (expanded to six movements ca. 1947) is influenced by European opera, while Três danças características (africanas e indígenas) of 1914–16 for piano, later arranged for octet and subsequently orchestrated, is radically influenced by the tribal music of the Caripunas Indians of Mato Grosso.
With his tone poems Amazonas (1916, first performed in Paris in 1929) and Uirapurú (1916, first performed 1935) he created works dominated by indigenous Brazilian influences. The works use Brazilian folk tales and characters, imitations of the sounds of the jungle and its fauna, imitations of the sound of the nose-flute by the violinophone, and not least imitations of the uirapuru itself.
Rossini

Gioachino Antonio Rossini (February 29, 1792 – November 13, 1868) was a popular Italian composer who created 39 operas as well as sacred music and chamber music. His best known works include Il barbiere di Siviglia (The Barber of Seville), La Cenerentola and Guillaume Tell (William Tell).
Rossini's most famous opera was produced on February 20, 1816 at the Teatro Argentina in Rome. The libretto by Cesare Sterbini, a version of Pierre Beaumarchais' infamous stage play Le Barbier de Séville, was the same as that already used by Giovanni Paisiello in his own Barbiere, an opera which had enjoyed European popularity for more than a quarter of a century. Much is made of how fast Rossini's opera was written, scholarship generally agreeing upon two weeks. Later in life, Rossini claimed to have written the opera in only twelve days. It was a colossal failure when it premiered as Almaviva; Paisiello’s admirers were extremely indignant, sabotaging the production by whistling and shouting during the entire first act. However, not long after the second performance, the opera became so successful that the fame of Paisiello's opera was transferred to Rossini's, to which the title The Barber of Seville passed as an inalienable heritage.
Rossini's most famous opera was produced on February 20, 1816 at the Teatro Argentina in Rome. The libretto by Cesare Sterbini, a version of Pierre Beaumarchais' infamous stage play Le Barbier de Séville, was the same as that already used by Giovanni Paisiello in his own Barbiere, an opera which had enjoyed European popularity for more than a quarter of a century. Much is made of how fast Rossini's opera was written, scholarship generally agreeing upon two weeks. Later in life, Rossini claimed to have written the opera in only twelve days. It was a colossal failure when it premiered as Almaviva; Paisiello’s admirers were extremely indignant, sabotaging the production by whistling and shouting during the entire first act. However, not long after the second performance, the opera became so successful that the fame of Paisiello's opera was transferred to Rossini's, to which the title The Barber of Seville passed as an inalienable heritage.
Vladimir Goncharenko

Vladimir Goncharenko russian contemporary artists,composer.
Chrono Crusade

Chrono Crusade, originally known in Japan as Chrno Crusade (Japanese: クロノクルセイド, Hepburn: Kurono Kuruseido), due to a typo, is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Daisuke Moriyama. It was originally published by Kadokawa Shoten in Comic Dragon, then a special issue of the Dragon Magazine. A 24-episode anime television series by Gonzo based on the manga ran from 2003 to 2004 on Fuji TV. The series was released in North America by ADV Manga and ADV Films, titled Chrono Crusade.Set in New York during the 1920s, Chrono Crusade follows the story of Rosette Christopher, and her demon partner Chrono. As members of the Magdalene Order, they travel around the country eliminating demonic threats to society, while Rosette searches for her lost brother, Joshua.
Frank Sinatra

Francis Albert "Frank" Sinatra (December 12, 1915 â May 14, 1998) was an American singer and actor.
Beginning his musical career in the swing era with Harry James and Tommy Dorsey, Sinatra became a solo artist with great success in the early to mid-1940s, being the idol of the "bobby soxers". His professional career had stalled by the 1950s, but it was reborn in 1954 after he won the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor.
He signed with Capitol Records and released several critically lauded albums (such as In the Wee Small Hours, Songs for Swingin' Lovers, Come Fly with Me, Only the Lonely and Nice 'n' Easy). Sinatra left Capitol to found his own record label, Reprise Records (finding success with albums such as Ring-A-Ding-Ding, Sinatra at the Sands and Francis Albert Sinatra & Antonio Carlos Jobim), toured internationally, and fraternized with the Rat Pack and President John F. Kennedy in the early 1960s. Sinatra turned 50 in 1965, recorded the retrospective September of My Years, starred in the Emmy-winning television special Frank Sinatra: A Man and His Music, and scored hits with "Strangers in the Night" and "My Way".
Sinatra attempted to weather the changing tastes in popular music, but with dwindling album sales and after appearing in several poorly received films, he retired in 1971. Coming out of retirement in 1973, he recorded several albums, scoring a hit with "(Theme From) New York, New York" in 1980, and toured both within the United States and internationally until a few years before his death in 1998.
Sinatra also forged a career as a dramatic actor, winning the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor for his performance in From Here to Eternity, and he was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Actor for The Man with the Golden Arm. His also starred in such musicals as High Society, Pal Joey, Guys and Dolls and On the Town. Sinatra was honored with the Kennedy Center Honors in 1983 and awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by Ronald Reagan in 1985 and the Congressional Gold Medal in 1997. Sinatra was also the recipient of eleven Grammy Awards, including the Grammy Trustees Award, Grammy Legend Award and the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award.
Beginning his musical career in the swing era with Harry James and Tommy Dorsey, Sinatra became a solo artist with great success in the early to mid-1940s, being the idol of the "bobby soxers". His professional career had stalled by the 1950s, but it was reborn in 1954 after he won the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor.
He signed with Capitol Records and released several critically lauded albums (such as In the Wee Small Hours, Songs for Swingin' Lovers, Come Fly with Me, Only the Lonely and Nice 'n' Easy). Sinatra left Capitol to found his own record label, Reprise Records (finding success with albums such as Ring-A-Ding-Ding, Sinatra at the Sands and Francis Albert Sinatra & Antonio Carlos Jobim), toured internationally, and fraternized with the Rat Pack and President John F. Kennedy in the early 1960s. Sinatra turned 50 in 1965, recorded the retrospective September of My Years, starred in the Emmy-winning television special Frank Sinatra: A Man and His Music, and scored hits with "Strangers in the Night" and "My Way".
Sinatra attempted to weather the changing tastes in popular music, but with dwindling album sales and after appearing in several poorly received films, he retired in 1971. Coming out of retirement in 1973, he recorded several albums, scoring a hit with "(Theme From) New York, New York" in 1980, and toured both within the United States and internationally until a few years before his death in 1998.
Sinatra also forged a career as a dramatic actor, winning the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor for his performance in From Here to Eternity, and he was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Actor for The Man with the Golden Arm. His also starred in such musicals as High Society, Pal Joey, Guys and Dolls and On the Town. Sinatra was honored with the Kennedy Center Honors in 1983 and awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by Ronald Reagan in 1985 and the Congressional Gold Medal in 1997. Sinatra was also the recipient of eleven Grammy Awards, including the Grammy Trustees Award, Grammy Legend Award and the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award.
Giacomo Puccini

Giacomo Puccini was an Italian composer known primarily for his operas. Regarded as the greatest and most successful proponent of Italian opera after Verdi, he was descended from a long line of composers, stemming from the late-Baroque era.
Mussorgsky

Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky (March 21, 1839 – March 28, 1881), one of the Russian composers known as the Five, was an innovator of Russian music. He strove to achieve a uniquely Russian musical identity, often in deliberate defiance of the established conventions of Western music.
Like his literary contemporary Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Mussorgsky depicts in his music "the insulted and the injured" with all their passion and pain. He raises these characters to tragic heights until the grotesque and majestic coexist. Mussorgsky could accomplish this not simply out of compassion or guilt towards them, but because in his works he almost becomes them. Mussorgsky's music is vivid, confused, feverish and ultimately hypnotizing —again, like Dostoyevsky at his best.
Many of his major works were inspired by Russian history, Russian folklore, and other nationalist themes, including the opera Boris Godunov, the orchestral tone poem Night on Bald Mountain, and the piano suite Pictures at an Exhibition. However, while Mussorgsky's music can be vivid and nationalistic, it does not glorify the powerful and is at times (such as in The Field-Marshal) antimilitaristic. For this reason, it was perceived as being directed against the state and its composer "under suspicion." He, like the others in The Russian Five, were considered dangerous extremists by the emperor and his court. This may have been the reason Tsar Alexander III personally crossed off Boris Godounov from the list of proposed pieces for the imperial opera in 1888.
For many years Mussorgsky's works were mainly known in versions revised or completed by other composers. Many of his most important compositions have recently come into their own in their original forms, and some of the original scores are now also available.
Like his literary contemporary Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Mussorgsky depicts in his music "the insulted and the injured" with all their passion and pain. He raises these characters to tragic heights until the grotesque and majestic coexist. Mussorgsky could accomplish this not simply out of compassion or guilt towards them, but because in his works he almost becomes them. Mussorgsky's music is vivid, confused, feverish and ultimately hypnotizing —again, like Dostoyevsky at his best.
Many of his major works were inspired by Russian history, Russian folklore, and other nationalist themes, including the opera Boris Godunov, the orchestral tone poem Night on Bald Mountain, and the piano suite Pictures at an Exhibition. However, while Mussorgsky's music can be vivid and nationalistic, it does not glorify the powerful and is at times (such as in The Field-Marshal) antimilitaristic. For this reason, it was perceived as being directed against the state and its composer "under suspicion." He, like the others in The Russian Five, were considered dangerous extremists by the emperor and his court. This may have been the reason Tsar Alexander III personally crossed off Boris Godounov from the list of proposed pieces for the imperial opera in 1888.
For many years Mussorgsky's works were mainly known in versions revised or completed by other composers. Many of his most important compositions have recently come into their own in their original forms, and some of the original scores are now also available.
Daniël van Goens

Daniël François van Goens (3 September 1858 – Paris, 10 May 1904) was a French cellist and composer of Dutch descent.He was the son of preacher François Corneille Jean van Goens (born in The Hague) and Angela Margaretha Charbon (born in Amsterdam). They would have about ten children, with three passing away from tuberculosis. He married pianist Germaine Polack, who was twenty years younger than him. She remarried Charles Lambert after his death and they had daughter Marie-Anne Lambert, the late mezzo-soprano Deva Dassy.He moved to France in his youth; his parents settled because of the climate in Montpellier, Van Goens was already there on the concert stage. The family later moved to Lausanne and in 1879 returned to Paris. Only one of his brothers remained in France, the late architect Jean Henri van Goens.
Laurent Salomon

Amateur musician, pianist and church organist since I was a child, then for a time choirmaster and harpsichordist, I like to discover new instruments, and new styles of music. I am fascinated by the inventiveness of musicians and instrument makers. Over the years, my curiosity has expanded to flutes, brass and string instruments and my inspiration combines classical, religious, jazz sources as well as songs. My compositions often stem from initial improvisations. I will appreciate your comments.
Brahms

Johannes Brahms (May 7, 1833 â April 3, 1897) was a German composer of the Romantic period. He was born in Hamburg and in his later years he settled in Vienna, Austria.
Brahms maintained a Classical sense of form and order in his works â in contrast to the opulence of the music of many of his contemporaries. Thus many admirers (though not necessarily Brahms himself) saw him as the champion of traditional forms and "pure music," as opposed to the New German embrace of program music.
Brahms venerated Beethoven: in the composer's home, a marble bust of Beethoven looked down on the spot where he composed, and some passages in his works are reminiscent of Beethoven's style. The main theme of the finale of Brahms's First Symphony is reminiscent of the main theme of the finale of Beethoven's Ninth, and when this resemblance was pointed out to Brahms he replied that any ass â jeder Esel â could see that.
Ein deutsches Requiem was partially inspired by his mother's death in 1865, but also incorporates material from a Symphony he started in 1854, but abandoned following Schumann's suicide attempt. He once wrote that the Requiem "belonged to Schumann". The first movement of this abandoned Symphony was re-worked as the first movement of the First Piano Concerto.
Brahms also loved the Classical composers Mozart and Haydn. He collected first editions and autographs of their works, and edited performing editions. He also studied the music of pre-classical composers, including Giovanni Gabrieli, Johann Adolph Hasse, Heinrich Schütz and especially Johann Sebastian Bach. His friends included leading musicologists, and with Friedrich Chrysander he edited an edition of the works of François Couperin. He looked to older music for inspiration in the arts of strict counterpoint; the themes of some of his works are modelled on Baroque sources, such as Bach's The Art of Fugue in the fugal finale of Cello Sonata No. 1, or the same composer's Cantata No. 150 in the passacaglia theme of the Fourth Symphony's finale.
Brahms maintained a Classical sense of form and order in his works â in contrast to the opulence of the music of many of his contemporaries. Thus many admirers (though not necessarily Brahms himself) saw him as the champion of traditional forms and "pure music," as opposed to the New German embrace of program music.
Brahms venerated Beethoven: in the composer's home, a marble bust of Beethoven looked down on the spot where he composed, and some passages in his works are reminiscent of Beethoven's style. The main theme of the finale of Brahms's First Symphony is reminiscent of the main theme of the finale of Beethoven's Ninth, and when this resemblance was pointed out to Brahms he replied that any ass â jeder Esel â could see that.
Ein deutsches Requiem was partially inspired by his mother's death in 1865, but also incorporates material from a Symphony he started in 1854, but abandoned following Schumann's suicide attempt. He once wrote that the Requiem "belonged to Schumann". The first movement of this abandoned Symphony was re-worked as the first movement of the First Piano Concerto.
Brahms also loved the Classical composers Mozart and Haydn. He collected first editions and autographs of their works, and edited performing editions. He also studied the music of pre-classical composers, including Giovanni Gabrieli, Johann Adolph Hasse, Heinrich Schütz and especially Johann Sebastian Bach. His friends included leading musicologists, and with Friedrich Chrysander he edited an edition of the works of François Couperin. He looked to older music for inspiration in the arts of strict counterpoint; the themes of some of his works are modelled on Baroque sources, such as Bach's The Art of Fugue in the fugal finale of Cello Sonata No. 1, or the same composer's Cantata No. 150 in the passacaglia theme of the Fourth Symphony's finale.
 Sheet Music Network is a site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.
Sheet Music Network is a site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.


