Cello Sheet Music
 "Music is the best means we have of digesting time." W. H. Auden
"Music is the best means we have of digesting time." W. H. Auden
The Beatles

The Beatles were a pop and rock group from Liverpool, England formed in 1960. Primarily consisting of John Lennon (rhythm guitar, vocals), Paul McCartney (bass guitar, vocals), George Harrison (lead guitar, vocals) and Ringo Starr (drums, vocals) throughout their career, The Beatles are recognised for leading the mid-1960s musical "British Invasion" into the United States. Although their initial musical style was rooted in 1950s rock and roll and homegrown skiffle, the group explored genres ranging from Tin Pan Alley to psychedelic rock. Their clothes, styles, and statements made them trend-setters, while their growing social awareness saw their influence extend into the social and cultural revolutions of the 1960s. After the band broke up in 1970, all four members embarked upon solo careers.
The Beatles are one of the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed bands in the history of popular music, selling over a billion records internationally. In the United Kingdom, The Beatles released more than 40 different singles, albums, and EPs that reached number one, earning more number one albums (15) than any other group in UK chart history. This commercial success was repeated in many other countries; their record company, EMI, estimated that by 1985 they had sold over one billion records worldwide. According to the Recording Industry Association of America, The Beatles have sold more albums in the United States than any other band. In 2004, Rolling Stone magazine ranked The Beatles number one on its list of 100 Greatest Artists of All Time. According to that same magazine, The Beatles' innovative music and cultural impact helped define the 1960s, and their influence on pop culture is still evident today. In 2008, Billboard magazine released a list of top-selling Hot 100 artists to celebrate the chart's fiftieth anniversary; The Beatles reached #1 again.
The Beatles are one of the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed bands in the history of popular music, selling over a billion records internationally. In the United Kingdom, The Beatles released more than 40 different singles, albums, and EPs that reached number one, earning more number one albums (15) than any other group in UK chart history. This commercial success was repeated in many other countries; their record company, EMI, estimated that by 1985 they had sold over one billion records worldwide. According to the Recording Industry Association of America, The Beatles have sold more albums in the United States than any other band. In 2004, Rolling Stone magazine ranked The Beatles number one on its list of 100 Greatest Artists of All Time. According to that same magazine, The Beatles' innovative music and cultural impact helped define the 1960s, and their influence on pop culture is still evident today. In 2008, Billboard magazine released a list of top-selling Hot 100 artists to celebrate the chart's fiftieth anniversary; The Beatles reached #1 again.
Mozart

Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, full name Johann Chrysostom Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 â 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical era. His over 600 compositions include works widely acknowledged as pinnacles of symphonic, concertante, chamber, piano, operatic, and choral music. Mozart is among the most enduringly popular of classical composers, and many of his works are part of the standard concert repertoire.
Mozart's music, like Haydn's, stands as an archetypal example of the Classical style. His works spanned the period during which that style transformed from one exemplified by the style galant to one that began to incorporate some of the contrapuntal complexities of the late Baroque, complexities against which the galant style had been a reaction. Mozart's own stylistic development closely paralleled the development of the classical style as a whole. In addition, he was a versatile composer and wrote in almost every major genre, including symphony, opera, the solo concerto, chamber music including string quartet and string quintet, and the piano sonata. While none of these genres were new, the piano concerto was almost single-handedly developed and popularized by Mozart. He also wrote a great deal of religious music, including masses; and he composed many dances, divertimenti, serenades, and other forms of light entertainment.
The central traits of the classical style can be identified in Mozart's music. Clarity, balance, and transparency are hallmarks of his work.
Mozart's music, like Haydn's, stands as an archetypal example of the Classical style. His works spanned the period during which that style transformed from one exemplified by the style galant to one that began to incorporate some of the contrapuntal complexities of the late Baroque, complexities against which the galant style had been a reaction. Mozart's own stylistic development closely paralleled the development of the classical style as a whole. In addition, he was a versatile composer and wrote in almost every major genre, including symphony, opera, the solo concerto, chamber music including string quartet and string quintet, and the piano sonata. While none of these genres were new, the piano concerto was almost single-handedly developed and popularized by Mozart. He also wrote a great deal of religious music, including masses; and he composed many dances, divertimenti, serenades, and other forms of light entertainment.
The central traits of the classical style can be identified in Mozart's music. Clarity, balance, and transparency are hallmarks of his work.
Saint Saens
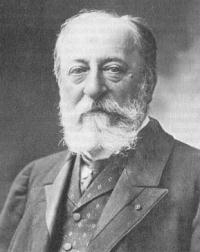
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (9 October 1835 – 16 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor, and pianist, known especially for The Carnival of the Animals, Danse Macabre, Samson and Delilah, Havanaise, Introduction and Rondo capriccioso, and his Symphony No. 3 (Organ Symphony).
Lady Gaga

Lady Gaga (born Stefani Joanne Angelina Germanotta on March 28, 1986) is an American recording artist. She began performing in the rock music scene of New York City's Lower East Side. She soon signed with Streamline Records, an imprint of Interscope Records, upon its establishment in 2007. During her early time at Interscope, she worked as a songwriter for fellow label artists and captured the attention of Akon, who recognized her vocal abilities, and had her also sign to his own label, Kon Live Distribution.
Her debut album, The Fame, was released on August 19, 2008. In addition to receiving generally positive reviews, it reached number-one in Canada, Austria, Germany, and Ireland and topped the Billboard Top Electronic Albums chart. Its first two singles, "Just Dance" and "Poker Face", co-written and co-produced with RedOne, became international number-one hits, topping the Hot 100 in the United States as well as other countries. The album later earned a total of six Grammy Award nominations and won awards for Best Electronic/Dance Album and Best Dance Recording. In early 2009, after having opened for New Kids on the Block and the Pussycat Dolls, she embarked on her first headlining tour, The Fame Ball Tour. By the fourth quarter of 2009, she released her second studio album The Fame Monster, with the global chart-topping lead single "Bad Romance", as well as having embarked on her second headlining tour of the year, The Monster Ball Tour.
Lady Gaga is inspired by glam rock musicians such as David Bowie and Freddie Mercury, as well as pop music artists such as Madonna and Michael Jackson. She has also stated fashion is a source of inspiration for her songwriting and performances. To date, she has sold over eight million albums and over thirty-five million singles worldwide.
Her debut album, The Fame, was released on August 19, 2008. In addition to receiving generally positive reviews, it reached number-one in Canada, Austria, Germany, and Ireland and topped the Billboard Top Electronic Albums chart. Its first two singles, "Just Dance" and "Poker Face", co-written and co-produced with RedOne, became international number-one hits, topping the Hot 100 in the United States as well as other countries. The album later earned a total of six Grammy Award nominations and won awards for Best Electronic/Dance Album and Best Dance Recording. In early 2009, after having opened for New Kids on the Block and the Pussycat Dolls, she embarked on her first headlining tour, The Fame Ball Tour. By the fourth quarter of 2009, she released her second studio album The Fame Monster, with the global chart-topping lead single "Bad Romance", as well as having embarked on her second headlining tour of the year, The Monster Ball Tour.
Lady Gaga is inspired by glam rock musicians such as David Bowie and Freddie Mercury, as well as pop music artists such as Madonna and Michael Jackson. She has also stated fashion is a source of inspiration for her songwriting and performances. To date, she has sold over eight million albums and over thirty-five million singles worldwide.
james newton howard

James Newton Howard (born June 9, 1951) is an American composer, conductor, and music producer. He has scored over 100 films and is the recipient of a Grammy Award, Emmy Award, and eight Academy Award nominations. His film scores include Pretty Woman (1990), The Fugitive (1993), The Devil's Advocate (1997), Dinosaur (2000), Atlantis: The Lost Empire (2001), Treasure Planet (2002), King Kong (2005), Batman Begins (2005), Blood Diamond (2006), The Dark Knight (2008), The Bourne Legacy (2012), The Hunger Games series (2012–2015) and Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them (2016). He has collaborated with directors M. Night Shyamalan, having scored nine of his films since The Sixth Sense, and Francis Lawrence, having scored all of his films since I Am Legend.
J. S. Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (21 March 1685, O.S.31 March 1685, N.S. – 28 July 1750, N.S.) was a German composer, organist, harpsichordist, violist, and violinist whose sacred and secular works for choir, orchestra, and solo instruments drew together the strands of the Baroque period and brought it to its ultimate maturity. Although he did not introduce new forms, he enriched the prevailing German style with a robust contrapuntal technique, an unrivalled control of harmonic and motivic organisation, and the adaptation of rhythms, forms and textures from abroad, particularly from Italy and France.
Revered for their intellectual depth, technical command and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg Concertos, the Goldberg Variations, the Partitas, The Well-Tempered Clavier, the Mass in B minor, the St Matthew Passion, the St John Passion, the Magnificat, A Musical Offering, The Art of Fugue, the English and French Suites, the Sonatas and Partitas for solo violin, the Cello Suites, more than 200 surviving cantatas, and a similar number of organ works, including the famous Toccata and Fugue in D minor and Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, as well as the Great Eighteen Chorale Preludes and Organ Mass.
Bach's abilities as an organist were highly respected throughout Europe during his lifetime, although he was not widely recognised as a great composer until a revival of interest and performances of his music in the first half of the 19th century. He is now generally regarded as one of the main composers of the Baroque style, and as one of the greatest composers of all time.
Revered for their intellectual depth, technical command and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg Concertos, the Goldberg Variations, the Partitas, The Well-Tempered Clavier, the Mass in B minor, the St Matthew Passion, the St John Passion, the Magnificat, A Musical Offering, The Art of Fugue, the English and French Suites, the Sonatas and Partitas for solo violin, the Cello Suites, more than 200 surviving cantatas, and a similar number of organ works, including the famous Toccata and Fugue in D minor and Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, as well as the Great Eighteen Chorale Preludes and Organ Mass.
Bach's abilities as an organist were highly respected throughout Europe during his lifetime, although he was not widely recognised as a great composer until a revival of interest and performances of his music in the first half of the 19th century. He is now generally regarded as one of the main composers of the Baroque style, and as one of the greatest composers of all time.
Apocalyptica

Apocalyptica is a Finnish cello metal band, composed of classically trained cellists and, since 2005, a drummer. Three of the cellists are graduates of the Sibelius Academy in Helsinki, Finland. Their music features elements from classical music, neo-classical metal, thrash metal, and symphonic metal.
Muse

Muse are a British rock band formed in Teignmouth, Devon, United Kingdom in 1994 under the alias of Rocket Baby Dolls. The band comprises Matthew Bellamy (vocals, guitar and piano), Christopher Wolstenholme (bass guitar and backing vocals) and Dominic Howard (drums and percussion). Muse's style can be considered as a mixture of many musical genres, most notably alternative rock, classical music and electronica. Muse are known best for their energetic and visually dazzling live performances and on June 16th & 17th, 2007 became the first band to sell out the newly built Wembley Stadium in London. Muse have released four studio albums with their first, Showbiz, released in 1999, followed by Origin of Symmetry in 2001 and Absolution in 2003. The most recent, Black Holes & Revelations (2006), was also the most critically acclaimed, garnering the band a Mercury Prize nomination and a third place finish in the NME Albums of the Year list for 2006. Muse have won various awards throughout their career including 5 MTV Europe Music Awards, 5 Q Awards, 4 NME Awards and 2 Brit awards.
Edvard Grieg

Edvard Hagerup Grieg (15 June 1843 – 4 September 1907) was a Norwegian composer and pianist who composed in the Romantic period. He is best known for his Piano Concerto in A minor, for his incidental music to Henrik Ibsen's play Peer Gynt (which includes Morning Mood and In the Hall of the Mountain King), and for his collection of piano miniatures Lyric Pieces. "Edvard" is sometimes mispelt as "Edward".
Grieg is renowned as a nationalist composer, drawing inspiration from Norwegian folk music. Early works include a symphony (which he later suppressed) and a piano sonata. He also wrote three sonatas for violin and piano and a cello sonata. His many short pieces for piano — often based on Norwegian folk tunes and dances — led some to call him the "Chopin of the North".
Concerto in A minor: 1. Allegro molto moderato
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 1. Allegro molto moderato
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Concerto in A minor: 2. Adagio
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 2. Adagio
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Concerto in A minor: 3. Allegro moderato molto e marcato
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 3. Allegro moderato molto e marcato
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Notturno, Op. 54, No. 4
Performed live by Mark Gasser
Problems listening to these files? See media help.
The Piano Concerto is his most popular work. Its champions have included the pianist and composer Percy Grainger, a personal friend of Grieg who played the concerto frequently during his long career. An arrangement of part of the work made an iconic television comedy appearance in the 1971 Morecambe and Wise Show, conducted by André Previn.
Some of the Lyric Pieces (for piano) are also well-known, as is the incidental music to Henrik Ibsen's play Peer Gynt, a play that Grieg found to be an arduous work to score properly. In a 1874 letter to his friend Frants Beyer, Grieg expressed his unhappiness with what is now considered one of his most popular compositions from Peer Gynt, In the Hall of the Mountain King: "I have also written something for the scene in the hall of the mountain King - something that I literally can't bear listening to because it absolutely reeks of cow-pies, exaggerated Norwegian nationalism, and trollish self-satisfaction! But I have a hunch that the irony will be discernible."
Grieg is renowned as a nationalist composer, drawing inspiration from Norwegian folk music. Early works include a symphony (which he later suppressed) and a piano sonata. He also wrote three sonatas for violin and piano and a cello sonata. His many short pieces for piano — often based on Norwegian folk tunes and dances — led some to call him the "Chopin of the North".
Concerto in A minor: 1. Allegro molto moderato
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 1. Allegro molto moderato
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Concerto in A minor: 2. Adagio
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 2. Adagio
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Concerto in A minor: 3. Allegro moderato molto e marcato
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 3. Allegro moderato molto e marcato
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Notturno, Op. 54, No. 4
Performed live by Mark Gasser
Problems listening to these files? See media help.
The Piano Concerto is his most popular work. Its champions have included the pianist and composer Percy Grainger, a personal friend of Grieg who played the concerto frequently during his long career. An arrangement of part of the work made an iconic television comedy appearance in the 1971 Morecambe and Wise Show, conducted by André Previn.
Some of the Lyric Pieces (for piano) are also well-known, as is the incidental music to Henrik Ibsen's play Peer Gynt, a play that Grieg found to be an arduous work to score properly. In a 1874 letter to his friend Frants Beyer, Grieg expressed his unhappiness with what is now considered one of his most popular compositions from Peer Gynt, In the Hall of the Mountain King: "I have also written something for the scene in the hall of the mountain King - something that I literally can't bear listening to because it absolutely reeks of cow-pies, exaggerated Norwegian nationalism, and trollish self-satisfaction! But I have a hunch that the irony will be discernible."
Damien Rice

Damien Rice (born December 7, 1973) is an Irish folk singer. He was born in Dublin, Ireland, to George and Maureen Rice and was raised in Celbridge, County Kildare, Ireland. He is also a distant relative of the famous Dubliner Katharine Rice.
He has released five albums: O, B-Sides, 9, Live At Fingerprints Warts & All, and Live from the Union Chapel.
Thanks to David Arnold, his second cousin, Rice was able to record O, which was released in 2003. O was dedicated to fellow Irish musician Mic Christopher. The album was a strong commercial success and won the Shortlist Music Prize.
Three years later, following extensive promotion of O in Ireland and further commercial success worldwide, Rice released his second studio album 9 in 2006. The album was recorded in 2004 and 2005, and released on November 3 in Ireland, on November 6 in Europe and the rest of the world and lastly on November 14 in North America.
He has released five albums: O, B-Sides, 9, Live At Fingerprints Warts & All, and Live from the Union Chapel.
Thanks to David Arnold, his second cousin, Rice was able to record O, which was released in 2003. O was dedicated to fellow Irish musician Mic Christopher. The album was a strong commercial success and won the Shortlist Music Prize.
Three years later, following extensive promotion of O in Ireland and further commercial success worldwide, Rice released his second studio album 9 in 2006. The album was recorded in 2004 and 2005, and released on November 3 in Ireland, on November 6 in Europe and the rest of the world and lastly on November 14 in North America.
Vivaldi

Antonio Lucio Vivaldi (March 4, 1678 â July 28, 1741), nicknamed il Prete Rosso ("The Red Priest"), was a Venetian priest and Baroque music composer, as well as a famous virtuoso violinist; he was born and raised in the Republic of Venice. The Four Seasons, a series of four violin concerti, is his best-known work and a highly popular Baroque piece.
Many of Vivaldi's compositions reflect a flamboyant, almost playful, exuberance. Most of Vivaldi's repertoire was rediscovered only in the first half of the 20th century in Turin and Genoa and was published in the second half. Vivaldi's music is innovative, breaking a consolidated tradition in schemes; he gave brightness to the formal and the rhythmic structure of the concerto, repeatedly looking for harmonic contrasts and innovative melodies and themes. Moreover, Vivaldi was able to compose nonacademic music, particularly meant to be appreciated by the wide public and not only by an intellectual minority. The joyful appearance of his music reveals in this regard a transmissible joy of composing; these are among the causes of the vast popularity of his music. This popularity soon made him famous in other countries such as France which was, at the time, very independent concerning its musical taste.
Vivaldi is considered one of the composers who brought Baroque music (with its typical contrast among heavy sonorities) to evolve into a classical style. Johann Sebastian Bach was deeply influenced by Vivaldi's concertos and arias (recalled in his Johannes Passion, Matthäuspassion, and cantatas). Bach transcribed a number of Vivaldi's concerti for solo keyboard, along with a number for orchestra, including the famous Concerto for Four Violins and Violoncello, Strings and Continuo (RV 580).
Many of Vivaldi's compositions reflect a flamboyant, almost playful, exuberance. Most of Vivaldi's repertoire was rediscovered only in the first half of the 20th century in Turin and Genoa and was published in the second half. Vivaldi's music is innovative, breaking a consolidated tradition in schemes; he gave brightness to the formal and the rhythmic structure of the concerto, repeatedly looking for harmonic contrasts and innovative melodies and themes. Moreover, Vivaldi was able to compose nonacademic music, particularly meant to be appreciated by the wide public and not only by an intellectual minority. The joyful appearance of his music reveals in this regard a transmissible joy of composing; these are among the causes of the vast popularity of his music. This popularity soon made him famous in other countries such as France which was, at the time, very independent concerning its musical taste.
Vivaldi is considered one of the composers who brought Baroque music (with its typical contrast among heavy sonorities) to evolve into a classical style. Johann Sebastian Bach was deeply influenced by Vivaldi's concertos and arias (recalled in his Johannes Passion, Matthäuspassion, and cantatas). Bach transcribed a number of Vivaldi's concerti for solo keyboard, along with a number for orchestra, including the famous Concerto for Four Violins and Violoncello, Strings and Continuo (RV 580).
Yiruma

Yiruma (born February 15 1978, Seoul, Korea) is a South Korean piano music composer. He is married to Son Hye-im.
Yiruma is well-known throughout the world, and his albums are sold all over Asia, as well as the United States and Europe. His most famous pieces are "Kiss the Rain", and also "River Flows in You". These pieces are widely mistaken for being associated with the movie Twilight. Although he formerly held dual citizenship as a citizen of the United Kingdom and South Korea, in July 2006 he gave up his British citizenship and entered the Republic of Korea Navy to begin his military service, which is compulsory for all male South Koreans. He has lived in Osaka, Japan for 5 years to promote album sales before giving up his dual citizenship.
Yiruma is well-known throughout the world, and his albums are sold all over Asia, as well as the United States and Europe. His most famous pieces are "Kiss the Rain", and also "River Flows in You". These pieces are widely mistaken for being associated with the movie Twilight. Although he formerly held dual citizenship as a citizen of the United Kingdom and South Korea, in July 2006 he gave up his British citizenship and entered the Republic of Korea Navy to begin his military service, which is compulsory for all male South Koreans. He has lived in Osaka, Japan for 5 years to promote album sales before giving up his dual citizenship.
Johann Sebastian Bach

Johann Sebastian Bach (31 March 1685 – 28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the Baroque period. He is known for instrumental compositions such as the Art of Fugue, the Brandenburg Concertos, and the Goldberg Variations, and for vocal music such as the St Matthew Passion and the Mass in B minor. Since the 19th-century Bach Revival he has been generally regarded as one of the greatest composers of the Western art musical canon.
Joe Hisaishi

Mamoru Fujisawa (藤澤 守 Fujisawa Mamoru?), known professionally as Joe Hisaishi (久石 譲 Hisaishi Jō?, born December 6, 1950), is a composer and director known for over 100 film scores and solo albums dating back to 1981.
While possessing a stylistically distinct sound, Hisaishi's music has been known to explore and incorporate different genres, including minimalist, experimental electronic, European classical, and Japanese classical. Lesser known are the other musical roles he plays; he is also a typesetter, author, arranger, and head of an orchestra.
He is best known for his work with animator Hayao Miyazaki, having composed scores for many of his films including Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind (1984), My Neighbor Totoro (1988), Princess Mononoke (1997), Spirited Away (2001), Howl's Moving Castle (2004) and Ponyo (2008). He is also recognized for the soundtracks he has provided for filmmaker 'Beat' Takeshi Kitano, including Dolls (2002), Kikujiro (1999), Hana-bi (1997), Kids Return (1996), Sonatine (1993).
While possessing a stylistically distinct sound, Hisaishi's music has been known to explore and incorporate different genres, including minimalist, experimental electronic, European classical, and Japanese classical. Lesser known are the other musical roles he plays; he is also a typesetter, author, arranger, and head of an orchestra.
He is best known for his work with animator Hayao Miyazaki, having composed scores for many of his films including Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind (1984), My Neighbor Totoro (1988), Princess Mononoke (1997), Spirited Away (2001), Howl's Moving Castle (2004) and Ponyo (2008). He is also recognized for the soundtracks he has provided for filmmaker 'Beat' Takeshi Kitano, including Dolls (2002), Kikujiro (1999), Hana-bi (1997), Kids Return (1996), Sonatine (1993).
Haydn

Franz Joseph Haydn (March 31, 1732 – May 31, 1809) was one of the most prominent composers of the classical period, and is called by some the "Father of the Symphony" and "Father of the String Quartet".
A life-long resident of Austria, Haydn spent most of his career as a court musician for the wealthy Hungarian Esterházy family on their remote estate. Isolated from other composers and trends in music until the later part of his long life, he was, as he put it, "forced to become original".
Although Haydn is still often called "Franz Joseph Haydn", the composer did not use the name "Franz" during his lifetime and this misnomer is avoided by modern scholars and historians. Joseph Haydn was the brother of Michael Haydn, himself a highly regarded composer, and Johann Evangelist Haydn, a tenor.
A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly.
Haydn's work was central to the development of what came to be called sonata form. His practice, however, differed in some ways from that of Mozart and Beethoven, his younger contemporaries who likewise excelled in this form of composition. Haydn was particularly fond of the so-called "monothematic exposition", in which the music that establishes the dominant key is similar or identical to the opening theme. Haydn also differs from Mozart and Beethoven in his recapitulation sections, where he often rearranges the order of themes compared to the exposition and uses extensive thematic development.
Perhaps more than any other composer's, Haydn's music is known for its humour. The most famous example is the sudden loud chord in the slow movement of his "Surprise" symphony; Haydn's many other musical jokes include numerous false endings (e.g., in the quartets Op. 33 No. 2 and Op. 50 No. 3), and the remarkable rhythmic illusion placed in the trio section of the third movement of Op. 50 No. 1.
A life-long resident of Austria, Haydn spent most of his career as a court musician for the wealthy Hungarian Esterházy family on their remote estate. Isolated from other composers and trends in music until the later part of his long life, he was, as he put it, "forced to become original".
Although Haydn is still often called "Franz Joseph Haydn", the composer did not use the name "Franz" during his lifetime and this misnomer is avoided by modern scholars and historians. Joseph Haydn was the brother of Michael Haydn, himself a highly regarded composer, and Johann Evangelist Haydn, a tenor.
A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly.
Haydn's work was central to the development of what came to be called sonata form. His practice, however, differed in some ways from that of Mozart and Beethoven, his younger contemporaries who likewise excelled in this form of composition. Haydn was particularly fond of the so-called "monothematic exposition", in which the music that establishes the dominant key is similar or identical to the opening theme. Haydn also differs from Mozart and Beethoven in his recapitulation sections, where he often rearranges the order of themes compared to the exposition and uses extensive thematic development.
Perhaps more than any other composer's, Haydn's music is known for its humour. The most famous example is the sudden loud chord in the slow movement of his "Surprise" symphony; Haydn's many other musical jokes include numerous false endings (e.g., in the quartets Op. 33 No. 2 and Op. 50 No. 3), and the remarkable rhythmic illusion placed in the trio section of the third movement of Op. 50 No. 1.
Charpentier
Marc-Antoine Charpentier, (born 1643, in or near Paris, France--died Feb. 24, 1704, Paris), most important French composer of his generation and the outstanding French composer of oratorios.
Charpentier went to Rome in about 1667, where he is believed to have studied composition, perhaps with Giacomo Carissimi. On his return to France about three years later he became chapelmaster to the dauphin but lost that position through Jean-Baptiste Lully's influence. He composed the music for a new version of Moliere's The Forced Marriage (first performed 1672) and collaborated with him again in The Imaginary Invalid (1673). After Moliere's death Charpentier continued to work for the Theatre Francais until 1685. He produced his greatest stage work, Medee, to Thomas Corneille's text, in 1693. From perhaps 1670 to 1688 he had as his patron Marie de Lorraine, known as Mademoiselle de Guise, and from 1679 he composed
Charpentier went to Rome in about 1667, where he is believed to have studied composition, perhaps with Giacomo Carissimi. On his return to France about three years later he became chapelmaster to the dauphin but lost that position through Jean-Baptiste Lully's influence. He composed the music for a new version of Moliere's The Forced Marriage (first performed 1672) and collaborated with him again in The Imaginary Invalid (1673). After Moliere's death Charpentier continued to work for the Theatre Francais until 1685. He produced his greatest stage work, Medee, to Thomas Corneille's text, in 1693. From perhaps 1670 to 1688 he had as his patron Marie de Lorraine, known as Mademoiselle de Guise, and from 1679 he composed
Beethoven

Ludwig van Beethoven (16 December 1770 - 26 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He was a crucial figure in the transitional period between the Classical and Romantic eras in Western classical music, and remains one of the most respected and influential composers of all time.
Born in Bonn, then in the Electorate of Cologne (now in modern-day Germany), he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. Beethoven's hearing gradually deteriorated beginning in his twenties, yet he continued to compose masterpieces, and to conduct and perform, even after he was completely deaf.
Born in Bonn, then in the Electorate of Cologne (now in modern-day Germany), he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. Beethoven's hearing gradually deteriorated beginning in his twenties, yet he continued to compose masterpieces, and to conduct and perform, even after he was completely deaf.
Gustav Holst

Gustav Theodore Holst (21 September 1874 – 25 May 1934) was an English composer and was a music teacher for nearly 20 years. He is most famous for his orchestral suite The Planets. Having studied at the Royal College of Music in London, his early work was influenced by Ravel, Grieg, Richard Strauss, and fellow student Ralph Vaughan Williams, but most of his music is highly original, with influences from Hindu spiritualism and English folk tunes. Holst's music is well known for unconventional use of metre and haunting melodies.
Holst wrote almost 200 catalogued compositions, including orchestral suites, operas, ballets, concertos, choral hymns, and songs (see Selected works below).
Holst became music master at St Paul's Girls' School in 1905 and director of music at Morley College in 1907, continuing in both posts until retirement.
He was the brother of Hollywood actor Ernest Cossart and father of the composer and conductor Imogen Holst, who wrote a biography of him in 1938.
Holst wrote almost 200 catalogued compositions, including orchestral suites, operas, ballets, concertos, choral hymns, and songs (see Selected works below).
Holst became music master at St Paul's Girls' School in 1905 and director of music at Morley College in 1907, continuing in both posts until retirement.
He was the brother of Hollywood actor Ernest Cossart and father of the composer and conductor Imogen Holst, who wrote a biography of him in 1938.
Nicola Porpora

Nicola (Antonio) Porpora (or Niccolò Porpora) (17 August 1686 – 3 March 1768) was an Italian composer of Baroque operas (see opera seria) and teacher of singing, whose most famous singing student was the castrato Farinelli. One of his other students was composer Matteo Capranica.
Ravel

Joseph-Maurice Ravel (March 7, 1875 – December 28, 1937) was a French composer of Impressionist music known especially for his melodies, orchestral and instrumental textures and effects. Much of his piano music, chamber music, vocal music and orchestral music has entered the standard concert repertoire.
Ravel's piano compositions, such as Jeux d'eau, Miroirs and Gaspard de la Nuit, demand considerable virtuosity from the performer, and his orchestral music, including Daphnis et Chloé and his arrangement of Modest Mussorgsky's Pictures at an Exhibition, uses a variety of sound and instrumentation very effectively.
Ravel is perhaps known best for his orchestral work, Boléro (1928), which he considered trivial and once described as "a piece for orchestra without music."
According to SACEM, Ravel's estate earns more royalties than that of any other French musician. According to international copyright law, Ravel's works are public domain since January 1, 2008 in most countries. In France, due to anomalous copyright law extensions to account for the two world wars, they will not enter the public domain until 2015.
Ravel's piano compositions, such as Jeux d'eau, Miroirs and Gaspard de la Nuit, demand considerable virtuosity from the performer, and his orchestral music, including Daphnis et Chloé and his arrangement of Modest Mussorgsky's Pictures at an Exhibition, uses a variety of sound and instrumentation very effectively.
Ravel is perhaps known best for his orchestral work, Boléro (1928), which he considered trivial and once described as "a piece for orchestra without music."
According to SACEM, Ravel's estate earns more royalties than that of any other French musician. According to international copyright law, Ravel's works are public domain since January 1, 2008 in most countries. In France, due to anomalous copyright law extensions to account for the two world wars, they will not enter the public domain until 2015.
Rossini

Gioachino Antonio Rossini (February 29, 1792 – November 13, 1868) was a popular Italian composer who created 39 operas as well as sacred music and chamber music. His best known works include Il barbiere di Siviglia (The Barber of Seville), La Cenerentola and Guillaume Tell (William Tell).
Rossini's most famous opera was produced on February 20, 1816 at the Teatro Argentina in Rome. The libretto by Cesare Sterbini, a version of Pierre Beaumarchais' infamous stage play Le Barbier de Séville, was the same as that already used by Giovanni Paisiello in his own Barbiere, an opera which had enjoyed European popularity for more than a quarter of a century. Much is made of how fast Rossini's opera was written, scholarship generally agreeing upon two weeks. Later in life, Rossini claimed to have written the opera in only twelve days. It was a colossal failure when it premiered as Almaviva; Paisiello’s admirers were extremely indignant, sabotaging the production by whistling and shouting during the entire first act. However, not long after the second performance, the opera became so successful that the fame of Paisiello's opera was transferred to Rossini's, to which the title The Barber of Seville passed as an inalienable heritage.
Rossini's most famous opera was produced on February 20, 1816 at the Teatro Argentina in Rome. The libretto by Cesare Sterbini, a version of Pierre Beaumarchais' infamous stage play Le Barbier de Séville, was the same as that already used by Giovanni Paisiello in his own Barbiere, an opera which had enjoyed European popularity for more than a quarter of a century. Much is made of how fast Rossini's opera was written, scholarship generally agreeing upon two weeks. Later in life, Rossini claimed to have written the opera in only twelve days. It was a colossal failure when it premiered as Almaviva; Paisiello’s admirers were extremely indignant, sabotaging the production by whistling and shouting during the entire first act. However, not long after the second performance, the opera became so successful that the fame of Paisiello's opera was transferred to Rossini's, to which the title The Barber of Seville passed as an inalienable heritage.
Albinoni

Tomaso Giovanni Albinoni (8 June 1671, Venice, Republic of Venice – 17 January 1751, Venice, Republic of Venice) was a Venetian Baroque composer. While famous in his day as an opera composer, he is mainly remembered today for his instrumental music, some of which is regularly recorded.
Andrew Lloyd Webber

Andrew Lloyd Webber, Baron Lloyd-Webber (born 22 March 1948) is an English composer of musical theatre, the elder son of organist William Lloyd Webber and brother of the cellist Julian Lloyd Webber. Lloyd Webber started composing at the age of six, and published his first piece at the age of nine.
Lloyd Webber has achieved great popular success, with several musicals that have run for more than a decade both in the West End and on Broadway. He has composed 13 musicals, a song cycle, a set of variations, two film scores, and a Latin Requiem Mass. He has also gained a number of honours, including a knighthood in 1992, followed by a peerage from the British Government for services to Music, seven Tony Awards (and 40 nominations), three Grammy Awards (with an additional 60 nominations), an Academy Award (two other nominations), seven Olivier Awards (with 100 nominations), a Golden Globe, and the Kennedy Center Honors in 2006. Several of his songs, notably "The Music of the Night" from The Phantom of the Opera, "I Don't Know How to Love Him" from Jesus Christ Superstar, "Don't Cry for Me, Argentina" from Evita, "Any Dream Will Do" from Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat and "Memory" from Cats have been widely recorded and were hits outside of their parent musicals. His company, the Really Useful Group, is one of the largest theatre operators in London.
Producers in several parts of the UK have staged productions, including national tours, of Lloyd Webber's musicals under licence from the Really Useful Group. According to britishhitsongwriters.com, he is the one hundredth most successful songwriter in U.K. singles chart history, based on weeks that his compositions have spent on the chart.
Lloyd Webber has achieved great popular success, with several musicals that have run for more than a decade both in the West End and on Broadway. He has composed 13 musicals, a song cycle, a set of variations, two film scores, and a Latin Requiem Mass. He has also gained a number of honours, including a knighthood in 1992, followed by a peerage from the British Government for services to Music, seven Tony Awards (and 40 nominations), three Grammy Awards (with an additional 60 nominations), an Academy Award (two other nominations), seven Olivier Awards (with 100 nominations), a Golden Globe, and the Kennedy Center Honors in 2006. Several of his songs, notably "The Music of the Night" from The Phantom of the Opera, "I Don't Know How to Love Him" from Jesus Christ Superstar, "Don't Cry for Me, Argentina" from Evita, "Any Dream Will Do" from Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat and "Memory" from Cats have been widely recorded and were hits outside of their parent musicals. His company, the Really Useful Group, is one of the largest theatre operators in London.
Producers in several parts of the UK have staged productions, including national tours, of Lloyd Webber's musicals under licence from the Really Useful Group. According to britishhitsongwriters.com, he is the one hundredth most successful songwriter in U.K. singles chart history, based on weeks that his compositions have spent on the chart.
Jean Sibelius

Jean Sibelius ( pronunciation (help·info)) (8 December 1865 – 20 September 1957) was a Finnish composer of the later Romantic period whose music played an important role in the formation of the Finnish national identity. His mastery of the orchestra has been described as "prodigious."
The core of Sibelius's oeuvre is his set of seven symphonies. Like Beethoven, Sibelius used each successive work to further develop his own personal compositional style. His works continue to be performed frequently in the concert hall and are often recorded.
In addition to the symphonies, Sibelius's best-known compositions include Finlandia, the Karelia Suite, Valse triste, the Violin Concerto in D minor and The Swan of Tuonela (one of the four movements of the Lemminkäinen Suite). Other works include pieces inspired by the Finnish national epic, the Kalevala; over 100 songs for voice and piano; incidental music for 13 plays; the opera Jungfrun i tornet (The Maiden in the Tower); chamber music; piano music; Masonic ritual music; and 21 separate publications of choral music.
The core of Sibelius's oeuvre is his set of seven symphonies. Like Beethoven, Sibelius used each successive work to further develop his own personal compositional style. His works continue to be performed frequently in the concert hall and are often recorded.
In addition to the symphonies, Sibelius's best-known compositions include Finlandia, the Karelia Suite, Valse triste, the Violin Concerto in D minor and The Swan of Tuonela (one of the four movements of the Lemminkäinen Suite). Other works include pieces inspired by the Finnish national epic, the Kalevala; over 100 songs for voice and piano; incidental music for 13 plays; the opera Jungfrun i tornet (The Maiden in the Tower); chamber music; piano music; Masonic ritual music; and 21 separate publications of choral music.
Richard Wagner

Wilhelm Richard Wagner (pronounced /ˈvɑːɡnər/, German pronunciation: ; 22 May 1813 – 13 February 1883) was a German composer, conductor, theatre director and essayist, primarily known for his operas (or "music dramas", as they were later called). Wagner's compositions, particularly those of his later period, are notable for their complex texture, rich harmonies and orchestration, and the elaborate use of leitmotifs: musical themes associated with individual characters, places, ideas or plot elements. Unlike most other opera composers, Wagner wrote both the music and libretto for every one of his stage works. Famous extracts from his operas include the "Ride of the Valkyries" and the Bridal Chorus from Lohengrin, popularly known as the wedding march "Here Comes the Bride".
Initially establishing his reputation as a composer of works such as The Flying Dutchman and Tannhäuser which were in the romantic traditions of Weber and Meyerbeer, Wagner transformed operatic thought through his concept of the Gesamtkunstwerk ("total work of art"). This would achieve the synthesis of all the poetic, visual, musical and dramatic arts, and was announced in a series of essays between 1849 and 1852. Wagner realised this concept most fully in the first half of the monumental four-opera cycle Der Ring des Nibelungen. However, his thoughts on the relative importance of music and drama were to change again and he reintroduced some traditional operatic forms into his last few stage works including Die Meistersinger von Nürnberg.
Wagner pioneered advances in musical language, such as extreme chromaticism and quickly shifting tonal centres, which greatly influenced the development of European classical music. His Tristan und Isolde is sometimes described as marking the start of modern music. Wagner's influence spread beyond music into philosophy, literature, the visual arts and theatre. He had his own opera house built, the Bayreuth Festspielhaus, which contained many novel design features. It was here that the Ring and Parsifal received their premieres and where his most important stage works continue to be performed today in an annual festival run by his descendants. Wagner's views on conducting were also highly influential. His extensive writings on music, drama and politics have all attracted extensive comment; not least for their frequently antisemitic content.
Wagner achieved all of this despite a life characterised, until his last decades, by political exile, turbulent love affairs, poverty and repeated flight from his creditors. His pugnacious personality and often outspoken views on music, politics and society made him a controversial figure during his life. He has remained one to this day. The impact of his his ideas can be traced in many of the arts throughout the twentieth century.
Initially establishing his reputation as a composer of works such as The Flying Dutchman and Tannhäuser which were in the romantic traditions of Weber and Meyerbeer, Wagner transformed operatic thought through his concept of the Gesamtkunstwerk ("total work of art"). This would achieve the synthesis of all the poetic, visual, musical and dramatic arts, and was announced in a series of essays between 1849 and 1852. Wagner realised this concept most fully in the first half of the monumental four-opera cycle Der Ring des Nibelungen. However, his thoughts on the relative importance of music and drama were to change again and he reintroduced some traditional operatic forms into his last few stage works including Die Meistersinger von Nürnberg.
Wagner pioneered advances in musical language, such as extreme chromaticism and quickly shifting tonal centres, which greatly influenced the development of European classical music. His Tristan und Isolde is sometimes described as marking the start of modern music. Wagner's influence spread beyond music into philosophy, literature, the visual arts and theatre. He had his own opera house built, the Bayreuth Festspielhaus, which contained many novel design features. It was here that the Ring and Parsifal received their premieres and where his most important stage works continue to be performed today in an annual festival run by his descendants. Wagner's views on conducting were also highly influential. His extensive writings on music, drama and politics have all attracted extensive comment; not least for their frequently antisemitic content.
Wagner achieved all of this despite a life characterised, until his last decades, by political exile, turbulent love affairs, poverty and repeated flight from his creditors. His pugnacious personality and often outspoken views on music, politics and society made him a controversial figure during his life. He has remained one to this day. The impact of his his ideas can be traced in many of the arts throughout the twentieth century.
Ennio Morricone
Ennio Morricone, OMRI (born November 10, 1928), is an Italian composer and conductor. He has composed and arranged scores for more than 500 film and television productions. Morricone is considered as one of the most influential film composers since the late 1950s. He is well-known for his long-term collaborations with international acclaimed directors such as Sergio Leone, Brian De Palma, Barry Levinson, and Giuseppe Tornatore.
He wrote the characteristic film scores of Leone's Spaghetti Westerns A Fistful of Dollars (1964), For a Few Dollars More (1965), The Good, the Bad and the Ugly (1966), Once Upon a Time in the West (1968), The Great Silence (1968), and My Name Is Nobody (1973). In the 80s, Morricone composed the scores for John Carpenter's horror movie The Thing (1982), Leone's Once Upon a Time in America (1984), Roland Joffé's The Mission (1986), Brian De Palma's The Untouchables (1987) and Giuseppe Tornatore's Cinema Paradiso (1988).
His more recent compositions include the scores for Oliver Stone's U Turn (1997), Tornatore's The Legend of 1900 (1998) and Malèna (2000), Mission to Mars (2000) by Brian De Palma, Fateless (2005), and Baaria - La porta del vento (2009). Ennio Morricone has won two Grammy Awards, two Golden Globes and five Anthony Asquith Awards for Film Music by BAFTA in 1979–1992. He has been nominated for five Academy Awards for Best Music, Original Score in 1979–2001. Morricone received the Honorary Academy Award in 2007 "for his magnificent and multifaceted contributions to the art of film music". He was the second composer to receive this award after its introduction in 1928.
He wrote the characteristic film scores of Leone's Spaghetti Westerns A Fistful of Dollars (1964), For a Few Dollars More (1965), The Good, the Bad and the Ugly (1966), Once Upon a Time in the West (1968), The Great Silence (1968), and My Name Is Nobody (1973). In the 80s, Morricone composed the scores for John Carpenter's horror movie The Thing (1982), Leone's Once Upon a Time in America (1984), Roland Joffé's The Mission (1986), Brian De Palma's The Untouchables (1987) and Giuseppe Tornatore's Cinema Paradiso (1988).
His more recent compositions include the scores for Oliver Stone's U Turn (1997), Tornatore's The Legend of 1900 (1998) and Malèna (2000), Mission to Mars (2000) by Brian De Palma, Fateless (2005), and Baaria - La porta del vento (2009). Ennio Morricone has won two Grammy Awards, two Golden Globes and five Anthony Asquith Awards for Film Music by BAFTA in 1979–1992. He has been nominated for five Academy Awards for Best Music, Original Score in 1979–2001. Morricone received the Honorary Academy Award in 2007 "for his magnificent and multifaceted contributions to the art of film music". He was the second composer to receive this award after its introduction in 1928.
Tchaikovsky

Pyotr Il'yich Tchaikovsky (May 7 1840 â November 6 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic era. While not part of the nationalistic music group known as "The Five", Tchaikovsky wrote music which, in the opinion of Harold Schonberg, was distinctly Russian: plangent, introspective, with modally-inflected melody and harmony.
Aesthetically, Tchaikovsky remained open to all aspects of Saint Petersburg musical life. He was impressed by Serov and Balakirev as well as the classical values upheld by the conservatory. Both the progressive and conservative camps in Russian music at the time attempted to win him over. Tchaikovsky charted his compositional course between these two factions, retaining his individuality as a composer as well as his Russian identity. In this he was influenced by the ideals of his teacher Nikolai Rubinstein and Nikolai's brother Anton.
Tchaikovsky's musical cosmopolitanism led him to be favored by many Russian music-lovers over the "Russian" harmonies and styles of Mussorgsky, Borodin and Rimsky-Korsakov.
Nonetheless he frequently adapted Russian traditional melodies and dance forms in his music, which enhanced his success in his home country. The success in St. Petersburg at the premiere of his Third Orchestral Suite may have been due in large part to his concluding the work with a polonaise. He also used a polonaise for the final movement of his Third Symphony.
Aesthetically, Tchaikovsky remained open to all aspects of Saint Petersburg musical life. He was impressed by Serov and Balakirev as well as the classical values upheld by the conservatory. Both the progressive and conservative camps in Russian music at the time attempted to win him over. Tchaikovsky charted his compositional course between these two factions, retaining his individuality as a composer as well as his Russian identity. In this he was influenced by the ideals of his teacher Nikolai Rubinstein and Nikolai's brother Anton.
Tchaikovsky's musical cosmopolitanism led him to be favored by many Russian music-lovers over the "Russian" harmonies and styles of Mussorgsky, Borodin and Rimsky-Korsakov.
Nonetheless he frequently adapted Russian traditional melodies and dance forms in his music, which enhanced his success in his home country. The success in St. Petersburg at the premiere of his Third Orchestral Suite may have been due in large part to his concluding the work with a polonaise. He also used a polonaise for the final movement of his Third Symphony.
Walt disney

Walter Elias Disney (/ˈdɪzni/; December 5, 1901 – December 15, 1966) was an American entrepreneur, animator, voice actor and film producer. A pioneer of the American animation industry, he introduced several developments in the production of cartoons. As a film producer, Disney holds the record for most Academy Awards earned by an individual, having won 22 Oscars from 59 nominations. He was presented with two Golden Globe Special Achievement Awards and an Emmy Award, among other honors. Several of his films are included in the National Film Registry by the Library of Congress.
Mitsumune Shinkichi

Shinkichi Mitsumune (光宗 信吉 Mitsumune Shinkichi) (born October 8, 1963) is a Japanese composer who writes music primarily for anime.
Mitsumune is a native of Fukuoka City in Fukuoka Prefecture and a graduate of Rikkyo University with a degree in business. He started studying music at the age of 4. After graduating from college, he toured music festivals across Japan as a keyboardist for a Marine band, and later for musicians such as Yukie Nishimura. Starting in 1995, he lent his skills to composing anime and movie scores with a full orchestra.
Mitsumune is a native of Fukuoka City in Fukuoka Prefecture and a graduate of Rikkyo University with a degree in business. He started studying music at the age of 4. After graduating from college, he toured music festivals across Japan as a keyboardist for a Marine band, and later for musicians such as Yukie Nishimura. Starting in 1995, he lent his skills to composing anime and movie scores with a full orchestra.
apocaliptica

Apocalyptica is a Finnish symphonic metal band from Helsinki, Finland, formed in 1993. The band is composed of classically trained cellists Eicca Toppinen, Paavo Lötjönen, and Perttu Kivilaakso (all three of whom are graduates of the Sibelius Academy in Helsinki), drummer Mikko Sirén, and vocalist Franky Perez. Originally a Metallica classical tribute band, the band eventually adopted a neoclassical metal style without the use of conventional guitars. They have sold over four million albums to date.
Debussy

Achille-Claude Debussy (August 22, 1862 – March 25, 1918) was a French composer. Along with Maurice Ravel, he is considered one of the most prominent figures working within the field of Impressionist music, though he himself intensely disliked the term when applied to his compositions. Debussy was not only among the most important of all French composers but also was a central figure in all European music at the turn of the twentieth century.
Debussy's music virtually defines the transition from late-Romantic music to twentieth century modernist music. In French literary circles, the style of this period was known as Symbolism, a movement that directly inspired Debussy both as a composer and as an active cultural participant.
Debussy's music virtually defines the transition from late-Romantic music to twentieth century modernist music. In French literary circles, the style of this period was known as Symbolism, a movement that directly inspired Debussy both as a composer and as an active cultural participant.
Shostakovich

Dmitri Dmitriyevich Shostakovich (25 September 1906 – 9 August 1975) was a Soviet Russian composer and one of the most celebrated composers of the 20th century.
Shostakovich achieved fame in the Soviet Union under the patronage of Leon Trotsky's chief of staff Mikhail Tukhachevsky, but later had a complex and difficult relationship with the Stalinist bureaucracy. In 1936, the government, most probably under orders from Stalin, harshly criticized his opera Lady Macbeth of the Mtsensk District, causing him to withdraw the Fourth Symphony during its rehearsal stages. Shostakovich's music was officially denounced twice, in 1936 and 1948, and was periodically banned. Nevertheless, he also received accolades and state awards and served in the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR. Despite the official controversy, his works were popular and well received.
Shostakovich achieved fame in the Soviet Union under the patronage of Leon Trotsky's chief of staff Mikhail Tukhachevsky, but later had a complex and difficult relationship with the Stalinist bureaucracy. In 1936, the government, most probably under orders from Stalin, harshly criticized his opera Lady Macbeth of the Mtsensk District, causing him to withdraw the Fourth Symphony during its rehearsal stages. Shostakovich's music was officially denounced twice, in 1936 and 1948, and was periodically banned. Nevertheless, he also received accolades and state awards and served in the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR. Despite the official controversy, his works were popular and well received.
Gustav Mahler

Gustav Mahler was an Austrian late-Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th century Austro-German tradition and the modernism of the early 20th century.
Astor Piazzolla

Ástor Pantaleón Piazzolla (March 11, 1921 – July 4, 1992) was an Argentine tango composer and bandoneón player. His oeuvre revolutionized the traditional tango into a new style termed nuevo tango, incorporating elements from jazz and classical music. An excellent bandoneonist, he regularly performed his own compositions with different ensembles.
Piazzolla's nuevo tango was distinct from the traditional tango in its incorporation of elements of jazz, its use of extended harmonies and dissonance, its use of counterpoint, and its ventures into extended compositional forms. As Argentine psychoanalyst Carlos Kuri has pointed out, Piazzolla's fusion of tango with this wide range of other recognizable Western musical elements was so successful that it produced a new individual style transcending these influences. It is precisely this success, and individuality, that makes it hard to pin down where particular influences reside in his compositions, but some aspects are clear. The use of the passacaglia technique of a circulating bass line and harmonic sequence, invented and much used in 17th and 18th century baroque music but also central to the idea of jazz "changes", predominates in most of Piazzolla's mature compositions. Another clear reference to the baroque is the often complex and virtuosic counterpoint that sometimes follows strict fugal behavior but more often simply allows each performer in the group to assert his voice. A further technique that emphasises this sense of democracy and freedom among the musicians is improvisation that is borrowed from jazz in concept, but in practice involves a different vocabulary of scales and rhythms that stay within the parameters of the established tango sound-world. Pablo Ziegler has been particularly responsible for developing this aspect of the style both within Piazzolla's groups and since the composer's death.
Piazzolla's nuevo tango was distinct from the traditional tango in its incorporation of elements of jazz, its use of extended harmonies and dissonance, its use of counterpoint, and its ventures into extended compositional forms. As Argentine psychoanalyst Carlos Kuri has pointed out, Piazzolla's fusion of tango with this wide range of other recognizable Western musical elements was so successful that it produced a new individual style transcending these influences. It is precisely this success, and individuality, that makes it hard to pin down where particular influences reside in his compositions, but some aspects are clear. The use of the passacaglia technique of a circulating bass line and harmonic sequence, invented and much used in 17th and 18th century baroque music but also central to the idea of jazz "changes", predominates in most of Piazzolla's mature compositions. Another clear reference to the baroque is the often complex and virtuosic counterpoint that sometimes follows strict fugal behavior but more often simply allows each performer in the group to assert his voice. A further technique that emphasises this sense of democracy and freedom among the musicians is improvisation that is borrowed from jazz in concept, but in practice involves a different vocabulary of scales and rhythms that stay within the parameters of the established tango sound-world. Pablo Ziegler has been particularly responsible for developing this aspect of the style both within Piazzolla's groups and since the composer's death.
Astor Piazolla

Astor Pantaleón Piazzolla (Spanish pronunciation: , Italian pronunciation: ; March 11, 1921 – July 4, 1992) was an Argentine tango composer, bandoneon player, and arranger. His oeuvre revolutionized the traditional tango into a new style termed nuevo tango, incorporating elements from jazz and classical music. A virtuoso bandoneonist, he regularly performed his own compositions with a variety of ensembles.
In 1992, American music critic Stephen Holden described Piazzolla as "the world's foremost composer of tango music".
In 1992, American music critic Stephen Holden described Piazzolla as "the world's foremost composer of tango music".
Ludwig van Beethoven

Ludwig van Beethoven (/ˈlʊdvɪɡ væn ˈbeɪt(h)oʊvən/ (About this soundlisten); German: (About this soundlisten); baptised 17 December 1770 – 26 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. A crucial figure in the transition between the classical and romantic eras in classical music, he remains one of the most recognized and influential musicians of this period, and is considered to be one of the greatest composers of all time.
Beethoven was born in Bonn, the capital of the Electorate of Cologne, and part of the Holy Roman Empire. He displayed his musical talents at an early age and was vigorously taught by his father Johann van Beethoven, and was later taught by composer and conductor Christian Gottlob Neefe. At age 21, he moved to Vienna and studied composition with Joseph Haydn. Beethoven then gained a reputation as a virtuoso pianist, and was soon courted by Prince Lichnowsky for compositions, which resulted in Opus 1 in 1795.
Beethoven was born in Bonn, the capital of the Electorate of Cologne, and part of the Holy Roman Empire. He displayed his musical talents at an early age and was vigorously taught by his father Johann van Beethoven, and was later taught by composer and conductor Christian Gottlob Neefe. At age 21, he moved to Vienna and studied composition with Joseph Haydn. Beethoven then gained a reputation as a virtuoso pianist, and was soon courted by Prince Lichnowsky for compositions, which resulted in Opus 1 in 1795.
Schubert

Franz Peter Schubert (January 31, 1797 – November 19, 1828) was an Austrian composer. He wrote some 600 lieder, nine symphonies (including the famous "Unfinished Symphony"), liturgical music, operas, and a large body of chamber and solo piano music. He is particularly noted for his original melodic and harmonic writing.
While Schubert had a close circle of friends and associates who admired his work (including his teacher Antonio Salieri, and the prominent singer Johann Michael Vogl), wider appreciation of his music during his lifetime was limited at best. He was never able to secure adequate permanent employment, and for most of his career he relied on the support of friends and family. Interest in Schubert's work increased dramatically in the decades following his death and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
While he was clearly influenced by the Classical sonata forms of Beethoven and Mozart (his early works, among them notably the 5th Symphony, are particularly Mozartean), his formal structures and his developments tend to give the impression more of melodic development than of harmonic drama. This combination of Classical form and long-breathed Romantic melody sometimes lends them a discursive style: his 9th Symphony was described by Robert Schumann as running to "heavenly lengths". His harmonic innovations include movements in which the first section ends in the key of the subdominant rather than the dominant (as in the last movement of the Trout Quintet). Schubert's practice here was a forerunner of the common Romantic technique of relaxing, rather than raising, tension in the middle of a movement, with final resolution postponed to the very end.
While Schubert had a close circle of friends and associates who admired his work (including his teacher Antonio Salieri, and the prominent singer Johann Michael Vogl), wider appreciation of his music during his lifetime was limited at best. He was never able to secure adequate permanent employment, and for most of his career he relied on the support of friends and family. Interest in Schubert's work increased dramatically in the decades following his death and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
While he was clearly influenced by the Classical sonata forms of Beethoven and Mozart (his early works, among them notably the 5th Symphony, are particularly Mozartean), his formal structures and his developments tend to give the impression more of melodic development than of harmonic drama. This combination of Classical form and long-breathed Romantic melody sometimes lends them a discursive style: his 9th Symphony was described by Robert Schumann as running to "heavenly lengths". His harmonic innovations include movements in which the first section ends in the key of the subdominant rather than the dominant (as in the last movement of the Trout Quintet). Schubert's practice here was a forerunner of the common Romantic technique of relaxing, rather than raising, tension in the middle of a movement, with final resolution postponed to the very end.
Pirates of the Caribbean

Pirates of the Caribbean is a Disney franchise encompassing numerous theme park attractions and a media franchise consisting of a series of films, and spin-off novels, as well as a number of related video games and other media publications. The franchise originated with the Pirates of the Caribbean theme ride attraction, which opened at Disneyland in 1967 and was one of the last Disney theme park attractions overseen by Walt Disney. Disney based the ride on pirate legends and folklore.
 Sheet Music Network is a site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.
Sheet Music Network is a site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.
